Audits and audit efficiency remain as important as companies change today. Indeed, an audit is an even more important enabler for our thriving capital markets. It embraces continuous innovation, applies agile auditing, and is focused on methodology and workflows based on risk.
Before knowing about the tools that are useful for Smart Contract Audit, let’s have a brief about the concept of Smart Contract and Smart Contract Audit.

What is a Smart Contract?
Table of Contents
A Smart Contract is software incorporating a set of rules to be followed for agreeing with the terms of an agreement, verifying the compliance automatically, and then finally implementing the terms which have been agreed upon. Simply put, it is a self-executing contract that excludes the dependency of a third party while the contract is made between two parties.
Consequently, two parties can directly transact with each other without involving any third-party dependence.
These smart contracts are trustable and distributed. These cannot tamper and no attacker can force any illegal activity.
Smart Contract Audit
Auditing a Smart Contract is going thoroughly through the code to avoid any data breach or any kind of bug present in the code. This is necessary because once this code is deployed, the code cannot be changed which can lead to enormous security risks, loss of data, and so on.
The procedure of auditing/testing a Smart Contract:
The process of auditing a code is similar to testing any code. There is a set of steps involved in the testing code.
- Testing of smart contract state changes
- Event testing
- Error testing
- Checking a message’s sender
Tools for Smart Contract Audit
Truffle
Truffle is a famous framework. It is a Node.js platform for compiling, linking, and deploying smart contracts. Several features are being provided by Truffle like custom deployment support, scriptable deployment, binary management, access to external packages, and so on.?
This framework is written in a user-friendly manner. Users, to be more specific engineers can make a choice for the functionality they need.?
To start using the Truffle framework, it must be installed via npm:
npm install -g truffle
Then, to create the project structure, a truffle init command must be made:
$ mkdir solidity-test-example
$ cd solidity-test-example/
$ truffle init
Truffle requires each contract to be stored in a separate file when you compile contracts. Also, the contract name is identical to the file name. Contracts are required to be stored in the Contracts/directory and tests are to be stored in the tests/directory.
Remix
A Remix is an online solidity IDE that is easy to use and completely featured by developers to check and compile smart contracts. There is an IDE version, as well as an online edition.?
Many of the tools within Remix include a solidity compiler that produces a lot of useful knowledge that can be used in different contexts.

It also features three runtime environments, namely injected Web3 to providers like Mist or MetaMask, Web3 provider to localhost via IPC, and Javascript VM, which is a simulated setting. The code analyzer supports developers in writing some of the best codes.
Sonar Solidity
To analyze the code, SonarSolidity is given to the SonaQube Console as a plugin. It clarifies flaws and glitches and can import Solium files, which can be expanded with Solium’s own plug-ins.?
This uses 25 rules that promote the best practices of Solidity and track bugs and problems with code smell.
Smart Anvil: An Open-Source tool for Smart Contracts
It is an open-source framework that conducts static smart contract analysis, deploys binary contract analysis, and is used for searching and querying blockchains. The open platform SmartAnvil is built around multiple components to cover the various aspects with a good study with contracts. While SmartAnvil can work in isolation, SmartAnvil communicates with Moose data and analysis tools application.
The below figure shows the key components of SmartAnvil
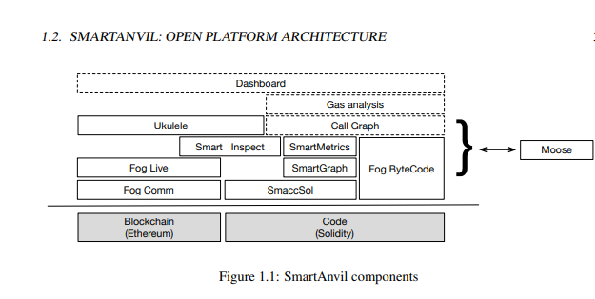
The picture is taken from the Duca18 SmartAnvil research paper
MythX
MythX is a cloud-based service that provides extra paying functionality as well as revenue-sharing when the paid subscription option goes live. The subscription model will be based upon a network of the stablecoin. The revenue-sharing model will allow everybody to earn through the development of MythX-fronted tools and integrations. The Truffle MythX plugin which is compliant with Truffle 5.0 or higher is one of the first end-user plugins. It is used in analyzing smart contracts to the Truffle framework.
Karl
Karl tests vulnerability code for smart contracts and can be used in real-time to track the Ethereum blockchain for newly deployed insecure smart contracts. By running candidate contracts in a simulated copy of the blockchain it removes false positives.?
Solgraph
It produces a DOT graph that visualizes a Solidity contract’s feature control flow and highlights possible security vulnerabilities.
Install it by entering the following command
npm install -g solgraph
Depending on permissions, here is the command to add an unsafe-perm flag
sudo npm install -g solgraph –unsafe-perm=true –allow-root
These are some commonly used tools for auditing/deploying smart contracts. Several other 3rd party tools are available in the ecosystem to enhance and optimize the contracts namely Sither, HEVM, Manticore, and many others. We at ImmuneBytes, understand the importance of using an external tool to find the hidden exploits in the contract and our team of auditors only use tools that apply to the Blockchain framework.
Few practices that prove to be best for Smart Contract Audit
Careful Deployment
- Catching bugs before a full production release is always easier.?
- Check contracts extensively, and add tests if new vectors of attack are identified?
- Grant bug bounties starting with alpha testnet releases?
- Implement in stages, with increased usage and testing at each point
Make contracts simple
- There are more chances of error when contracts are complex.
- Make sure the rationale behind the contract is simple.
- Try to use already-written code wherever possible
Stay updated
- As soon as any bug is found, remove it and update the deployed software.
- Update to the new version as soon as a new version of any library is discovered.
- Must adopt the latest security techniques.
Repetition vs Reuse
- From a software engineering perspective, a smart contract framework wishes to optimize reuse where possible. Solidity offers many ways to reuse contract code. Using proven pre-deployed contracts that you own is generally the safest way to achieve reuse of code.?
- In cases where self-owned previously deployed contracts are not available, replication is sometimes invoked. Efforts like the Solidity Library of OpenZeppelin aim to include patterns in such a way that stable code can be reused without duplication. Any analysis of contract security must include any reused code that has not previously established a confidence level commensurate with the funds at risk in Smart Contracts.
Be Prepared for Failure Beforehand
- Any contract that is not insignificant will have errors therein. So the code must be able to react gracefully to bugs and vulnerabilities.?
- If things go wrong stop the contract (‘circuit breaker’).
- Manage the amount of money at risk (rate cap, overall utilization).?
- Have an easy route to update bug fixes and enhancements.
So, keeping in mind the requirements of users as well as the enormous benefits of auditing smart contracts, we at ImmuneBytes inculcate this feature in our service. You should consider reaching out to us if you are in search of an external auditor.