Overview
Table of Contents
Mango Markets, a Decentralized Exchange (DEX) on the Solana blockchain, experienced an exploit on 11 Oct 2022, which left it with losses to the tune of $116 million in the form of irretrievable debt.
The exploit resulted from a price manipulation on the native MNGO token that left Mango’s treasury with a negative balance of 116.7 million.
The platform’s reliance on Oracles and its zero-fee model were also the primary contributors to the cause of the manipulation.
About Mango Markets
Mango Markets was a prominent Decentralized Exchange (DEX) operating on the Solana blockchain. The platform uniquely facilitated spot markets, perpetual futures, and lending services, enabling users to employ cross-margin trading with leverage of up to 5x.
A defining feature of Mango Markets was its margin trading protocol, which used oracles to fetch real-time spot prices, allowing users to engage in cross-margin trades.
Root Cause
The primary cause was the vulnerability and reliance on oracles, which, despite their sophisticated multi-source average pricing mechanism, failed to prevent manipulative price inflation. Additionally, the lack of an insurance fund due to the zero-fee model put the entire ecosystem at risk. The attacker used Mango’s intrinsic features, specifically cross-margin trades, for market manipulation.
In the blockchain universe, an oracle is akin to a data bridge between the digital and real world. They fetch real-time data, like spot prices from various exchanges, determining an asset’s value on the platform.
Attack Flow
The hacker used two accounts to carry out the attack. The first account was used for going short, and the second was used for hedging positions.
The attack was orchestrated as follows:
- Two wallets were initialized, each funded with $5,000,000 USDC.
https://explorer.solana.com/tx/66AFLig3vs5XkksTZRh5BPo2iiiPV7jHL3hhjwMe3mRyqC9FG8ELgx3HPCWs8QQy1iSi9BAzm6Wx24fHcTtC1xyC)
https://explorer.solana.com/tx/3cBEK257espSw2X6Z7ZZESPPdcsfBoNLYJGAmXEExxw1QpjkSJfcd9kmtER7LkZ3RGbeXKHv1FR4hRBCD5wA8unY - Wallet 1 placed a sell offer for 483 million $MNGO perpetual futures at 3.8 cents per future. https://trade.mango.markets/account?pubkey=CQvKSNnYtPTZfQRQ5jkHq8q2swJyRsdQLcFcj3EmKFfX
- Wallet 2 stepped in to purchase the entirety of the $MNGO perpetual futures from Wallet 1 at $0.0382/unit. https://trade.mango.markets/account?pubkey=4ND8FVPjUGGjx9VuGFuJefDWpg3THb58c277hbVRnjNa
- Manipulation Phase: The attacker instigated purchases of spot $MNGO across multiple exchanges, including Mango Markets, AscendEX, and FTX, inducing the price to spike to a staggering $.91.
- Settling Accounts: Profits and losses between Wallet 1 and Wallet 2 were balanced, leading to Wallet 2 amassing an immense unrealized profit due to the 483 million long position.
- Price Elevation: The price of MNGO increased by approximately 2,394% ( from $0.038 to a peak of $0.91), which in turn raised the collateral value of the hacker’s account.
- Loan Acquisition: Capitalizing on the exaggerated unrealized profit, the attacker secured a loan amounting to $116 million in crypto tokens.
- Final Extraction: The loaned crypto assets were promptly withdrawn, using the unrealized gains as collateral.
The Aftermath of the Exploit
Soon after the exploit, Mango Markets were frozen to prevent further deposits. The hack has resulted in a 23% drop in the total value of assets locked in the Solana system, which fell below the $1B mark for the first time since July 2021.
The exploiter, later identified as Avraham Eisenberg, justified his actions by posting a tweet stating that he did not do anything illegal and had used legal open market actions to make a legitimate profit.
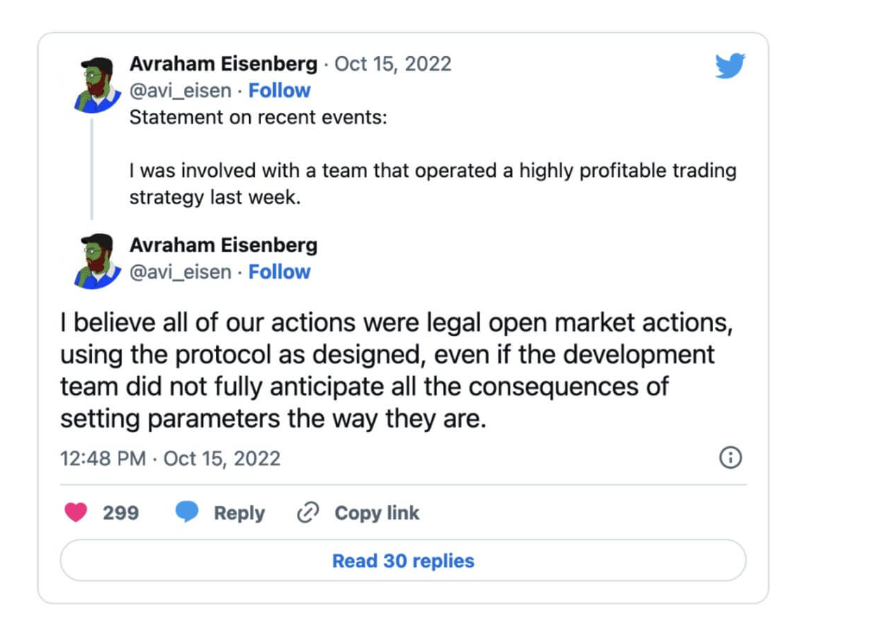
Later, he approached the DAO of Mango Markets with a reimbursement proposition in which they proposed to return most of the stolen funds if the community agreed to repay their bad debt incurred during an operation to save a different Solana project called Solend, in the month of June.
He also proposed a return of funds if he was allowed to retain $70 million of the stolen funds without the possibility of criminal prosecution.
The Mango Markets team did not agree to this proposal by hackers and instead offered $47 million as a bug bounty if the exploiters agreed to return the remaining funds of $67 million.
They also assure the exploiters that they would waive off any potential claims against accounts with bad debt and not pursue any criminal investigations or freezing of funds once stolen tokens are returned.
While the agreement with the exploiter initially appeared to be consensual, it soon became a focal point of controversy,
Further intensifying the situation, Mango Markets took the unprecedented step of filing a civil lawsuit on January 25th. The lawsuit, directed against an individual named Eisenberg, accused him of masterminding the exploit. The litigation seeks a restitution amounting to $47 million and contests the legitimacy of the prior agreement with the DAO, positing it was made under coercion.
The exploiter Avraham Eisenberg was subsequently arrested in New York on charges of market manipulation, which could attract imprisonment of 25 years.
Similar Exploits
On Dec 10, 2022, Lodestar Finance was exploited for $5.8 million. The exploiter’s modus operandi resembled the ‘Mango Markets’ manipulator.
Here also, the hackers artificially inflated the price of an illiquid collateral asset, which was used as collateral to take loans, which were never settled, and the protocol was left with irretrievable debt in the end.
Mitigation Steps to Avoid Such Manipulations
- Enhance oracles to reduce vulnerability to price manipulation.
- Implement robust trade monitoring mechanisms.
- Consider establishing an insurance fund.
- Limit high-leverage trades concerning low-liquidity assets.
- Incorporate real-time chain monitoring to flag suspicious activities.
Conclusion
The Mango Markets exploit is a stark reminder of the inherent vulnerabilities in the DeFi ecosystem. While these platforms promise decentralization, transparency, and empowerment, they can still fall prey to well-planned exploits. It is paramount for platforms to evolve and enhance security measures continuously.
Rigorous testing, community engagement, transparency, regular updates, and collaboration are some ways to ensure a safer ecosystem for all stakeholders.
ImmuneBytes specializes in identifying weaknesses in smart contracts, and their expertise could have been invaluable in averting such an exploit. It underscores the critical role that specialized smart contract auditing firms play in ensuring the security and robustness of DeFi platforms.

