The world moved on and Ethereum became slow. That was the start of newer and faster cryptocurrencies entering the market. People started switching over to eth because of Ethereum’s high gas and low transaction speed.
Traditionally a period of optimism and positive market sentiment, there is a growing sense that we are moving into what the bankless called the great Layer 2, the gold rush. Polygon and Arbitrum are two big names in this sector.
In today’s article, we’re going to look at how the two, Polygon and Arbitrum, are different from each other! Try not to get too dizzy. Let’s go!
An Introduction to Polygon
Table of Contents
We already have a blog dedicated solely to Polygon Network, discussing its working, features, and technical know-how.
Polygon is an Indian blockchain scalability platform called ‘the Ethereum’s Internet of Blockchains‘. It aims to bring the adaptability and scalability of alt chains along with Ethereum’s security, liquidity, and interoperability.
While Matic was designed as a simple layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum, Polygon is the infrastructure for a network of massively scaling, collaborative blockchains that retain their self-sovereignty.
This multi-chain system is akin to other ones such as Polkadot, Cosmos, Avalanche, etc, but with at least three major upsides:
- It can fully benefit from Ethereum’s network effects
- It is inherently more secure
- It is more open and powerful
Recommend Read: Polygon (Matic) Network
Now let’s take a look at Arbitrum.
An Introduction to Arbitrum
Arbitrum is a layer 2 solution designed to improve the capabilities of Ethereum smart contracts — boosting their speed and scalability while adding additional privacy features to boot.
It’s built to address some of the shortcomings of current Ethereum-based smart contracts — such as poor efficiency and high execution costs — which have damaged the Ethereum user experience and frequently make transacting an expensive task.
Arbitrum uses a technique known as transaction rollups to record batches of submitted transactions on the Ethereum main chain, and execute them on cheap, scalable layer 2 sidechains while leveraging Ethereum to ensure correct results. This process helps to offload most of the computational and storage burden Ethereum currently suffers from while enabling new classes of powerful layer 2-based DApps.
Recommend Read: Arbitrum bridge tutorial
Difference Between Polygon & Arbitrum?
Polygon is technically a side chain and not a layer 2. What’s the difference?
In Polygon’s case, it’s a POS consensus where validators can state Matic tokens and run a full node.
Since the time Polygon was launched in April, securing more than 11 billion dollars in total value locked in its protocol, it has made massive gains. However, the issue with its system is not getting funds back to Ethereum. So if you’re using Polygon, you have to swap ETH for the protocol’s native Matic token over a chain bridge.
The chain bridge uses a lock and mint mechanism, so you deposit ETH into the chain bridge, and that each gets locked into a smart contract. Once it’s locked, Polygon then mints an equal amount of Matic tokens when going through the chain bridge the other way from Matic to ETH. Matic tokens are burned, all destroyed, and then the ETH is released from the smart contract.
So, they all work kind of the same way. Depending on which chain bridge you use, transactions could take several hours to a week. For instance, using the plasma bridge which inherits its security from the Ethereum main chain these swaps take seven days.
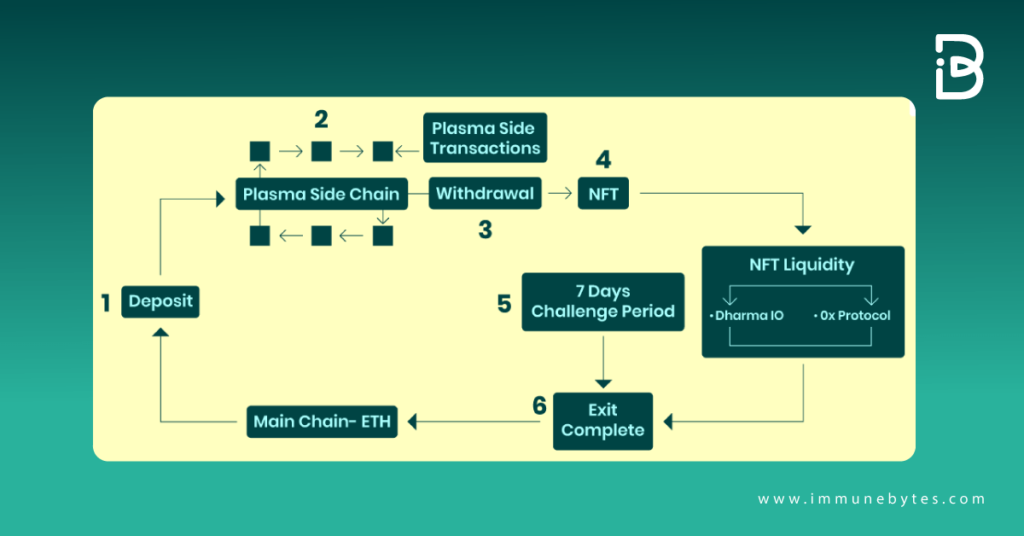
Recommend Read: POLYGON BRIDGE: TRANSFER ETH FROM ETHEREUM MAINNET TO POLYGON MAINNET
Users can also utilize the pos bridge, which is secured by the same set of validators that have staked Matic to verify transactions on the sidechain, and as such, that swap will take roughly three hours.
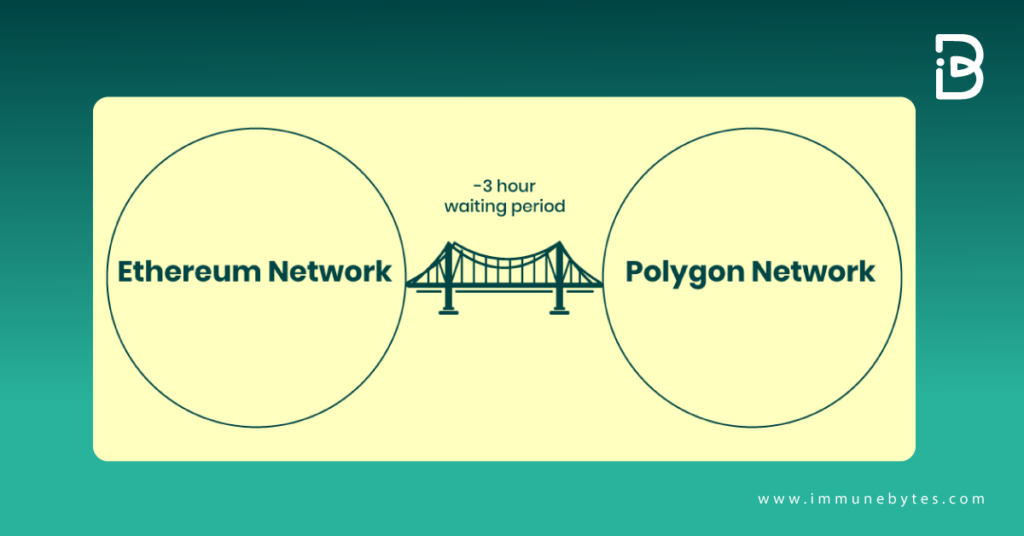
Some Polygon users have complained about the slow return journey, not to mention concerns over the chain’s perceived centralization vulnerabilities.
And that now brings us neatly to Arbitrum!
Arbitrum takes data storage and computation and moves it off of the Ethereum mainchain. By processing transactions in a separate environment, via the ArbOS, Arbitrum can clear transactions more quickly and it’s not affected by network congestion on Ethereum.
Arbitrum transactions are expected to cost about 1/10th or less of what they would cost on the Ethereum main chain.
To take advantage of Arbitrum’s fast transactions and low fees, an Ethereum user has to send their ETH or ERC20 token to the Arbitrum deposit contract. Once the deposit transaction is confirmed, the user can access their coins from within the Arbitrum ecosystem.
It’s important to differentiate between the Arbitrum and Ethereum ecosystems. Projects that are currently running on Ethereum are not automatically included in Arbitrum. Developers have to build their application into Arbitrum if they want it to work there.
Apart from their work, here are some of the key differences between the two.
- The primary difference between Arbitrum and Polygon is the security mechanism. Arbitrum is secured by the Ethereum base layer and does not have its token. Polygon is secured by its Proof of Stake consensus mechanism, where stakers lock up the MATIC token to get a reward for validating transactions.
- Transaction fees on Arbitrum are slightly higher than Polygon, although the fees on both networks are significantly cheaper than Ethereum base layer fees.
- In terms of decentralization, a good argument can be made that Arbitrum is more decentralized since it’s secured by Ethereum’s widely distributed network of miners. Polygon is secured by MATIC staking, which is a smaller pool of capital versus the miners who are securing Ethereum.
- Polygon’s main advantage is fast withdrawals. Unlike Arbitrum where withdrawals can take two weeks, withdrawals on Polygon using the Proof of Stake bridge take just three hours.
Concluding Thoughts
Arbitrum and Polygon haven’t yet noticeably improved the scalability of Ethereum. However, they do carry the potential in them. Once developers start porting over to either one of the solutions, the protocols will rise.
It will be exciting to watch what features, other than scalability and security, these protocols bring for the users and how many of them will adopt them, and also to see how the differences between Arbitrum and Polygon play out in their future success.
About Us
ImmuneBytes is facilitating blockchain security audits by employing the use of cutting-edge techniques on smart contracts and decentralized applications. We have a team of experienced security professionals who are adept at their niches and provide you with innovative solutions and consultation. So far we have worked on 175+ blockchain start-ups on different blockchain frameworks, with clients spread across the globe, and are continually unfolding ourselves to make this decentralized movement thrive.

