With Decentralized exchanges becoming a household name in the recent few months, it has become immensely vital to know about the factors that have shaped their popularity as well as how to establish a secure DEX.
DEXs offer new models of equitable stakeholder participation and governance. It is a reliable way to link buyers and sellers. Some of the most widely-used DEXs today are DexGuru, dYdX, Uniswap, PancakeSwap, Curve Finance, etc. Keeping in mind the never-ending list of crypto hacks on the exchanges these days, it has become indispensable to carry out DEX security audits.
We, at ImmuneBytes, are pioneers in providing DEX smart contract audit services to clients worldwide to make the financial world a better place for everyone. With our professional DEX audit reports, we have saved many of our clients from potential crypto hacks.
Are you well aware of decentralized exchanges? Worry not, we?re here to help you!
This blog will run you through the introduction to DEX, the difference between CEX and DEX, how DEX works, DEX types, how to use DEX, and the pros and cons of using DEX
So without any further ado, let’s get started.
What is DEX?
Table of Contents
As the name suggests, a decentralized exchange (DEX) doesn’t have a central authority. It is a peer-to-peer marketplace that allows users to trade cryptocurrencies without any intermediary to facilitate the transaction and look after the funds.
DEXs use blockchain-based smart contracts to replace traditional intermediaries, such as banks, brokers, payment processors, and other organizations, to enable the exchange of assets.
DEXs are a cornerstone of decentralized finance (DeFi). DEXs offer complete transparency into the fund movement and all the mechanisms responsible for facilitating the exchange. Because the user funds do not pass through the crypto wallet of any third party, the centralization risks get eliminated within the crypto ecosystem. This enhances DEX cybersecurity. Due to its permissionless composability, DEXs are a key “money LEGO” upon which more complex financial products can be built.
How are DEX and CEX different?
Let us see the difference between a decentralized and a centralized exchange.
| Decentralized Exchange (DEX) | Centralized Exchange (CEX) |
| Users do not need to transfer their cryptocurrencies to the exchange wallets. | Users need to transfer their cryptocurrencies to the exchange wallets. |
| There is no intermediary or central authority to look after the funds or transactions. | There is an intermediary or central authority that looks after the funds and transactions. |
| There is an absence of KYC requirements to trade here. | It requires KYC requirements to trade here. |
This is the essential crux of both exchanges. Now, we can proceed with the working of a DEX to get an insight into DEX security.
How does a Decentralized Exchange (DEX) Work?
Blockchains support smart contracts where users store their funds. The user has to pay a transaction and a trading fee. These decentralized exchanges (DEX) are built on top of these networks. Traders interact with smart contracts to use DEX.
The designs of the DEX vary in terms of benefits in the form of decentralization, feature sets, and scalability.
Users need to pay both the network and trading fees. While trading fees are collected by the underlying protocol, its liquidity providers, token holders, or a combination of these organizations, as stated by the protocol’s design, network fees refer to the gas cost of the on-chain transaction.
A decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) that contains all the community’s stakeholders governs the protocol administrative rights and decisions by voting. The central vision behind these exchanges is to have End-to-end on-chain infrastructure that is permissionless accessible, has decentralized ownership among a group of stakeholders, has no single point of failure, and is end-to-end.
Now, let us discuss how many types of decentralized exchanges (DEX) exist.
Types of Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
You can come across three main types of decentralized exchanges which are as follows:
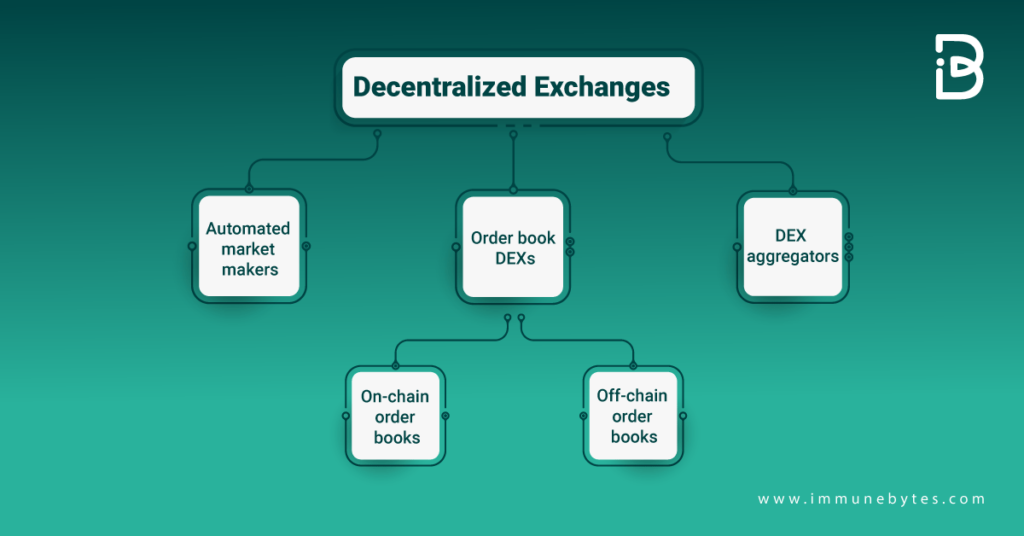
Let us discuss each of these types briefly.
Automated Market Makers (AMM)
This system relies on the fact that the purpose of a smart contract is to solve the liquidity problem. These AMMs rely on blockchain-based services known as blockchain oracles to determine the price of traded assets by gathering data from exchanges and other platforms. The smart contracts of these decentralized exchanges use pre-funded pools of assets known as liquidity pools rather than matching purchase orders and sell orders.
Order book DEXs
Order books keep track of all open purchase and sell orders for specific asset pairs. Sell orders show that a trader is prepared to ask for a special price to sell an asset, whereas buy orders show that a trader is eager to acquire or bid for an asset at that price. The size of the order book and the market price on the exchange is determined by the difference between these values.
When DEXs use to order books, the open order information is frequently kept on-chain while user funds are kept in their wallets. These exchanges might permit traders to use money lent to them by lenders on their platform to leverage their bets. By enlarging the position size with borrowed money, which must be repaid even if the traders lose their bet, leveraged trading raises the profit potential of a trade but also increases the danger of liquidation.
To give traders the advantages of centralized exchanges, DEX systems, which keep their order books off the blockchain, only settle trades there. Off-chain order books enable exchanges to operate more quickly and cheaply while ensuring that trades are performed at the pricing consumers want.
It is crucial to note that order book DEXs frequently experience liquidity problems. Traders typically stay to centralized platforms because they effectively compete with centralized exchanges and incur additional costs due to what is paid to transact on-chain. DEXs with off-chain order books lower these expenses, but because money must be deposited in them, there are hazards associated with smart contracts.
DEX Aggregators
To solve the issues related to liquidity, DEX aggregators use a wide range of mechanisms and protocols. To minimize slippage on large orders, optimize swap fees and token prices, and provide traders with the lowest price in the shortest amount of time, these platforms essentially pool liquidity from many DEXs.
How to use DEX?
There is no sign-up process for DEX. Instead, if you’re a trader, you need to have a wallet compatible with the smart contracts on the network of the exchanges. The decentralized exchanges’ financial services can be accessed easily if you have a smartphone and an internet connection.
These are the steps that you need to follow to use a DEX.
- Decide the network that you want to use.
- Choose a wallet that is compatible with the network that you have selected.
- Fund it with its native token to pay the transaction fees.
- Buy the tokens on centralized exchanges.
- Withdraw the tokens to their wallets.
- Click the “Connect Wallet” on the website of DEX.
Pros of using a Decentralized Exchange
It is expensive to trade on DEXs, especially if the transaction fees on the network are high. Nevertheless, who doesn?t like the idea of secure DEX crypto? The list of advantages of using a DEX is as follows:
Token Availability
Unlike decentralized exchanges, DEXs have the advantage of including any token minted on the blockchain. This means that all the new projects are likely to get listed on them way before getting listed on CEXs.
Additional Read: Crypto Security Audit
Anonymity
When users trade one cryptocurrency for other on DEX, their anonymity is preserved. This is unlike CEX; users don’t need to complete KYC processes in DEX. As a result, many people who do not wish their identities to be revealed get attracted to DEXs.
Additional Read: What is Anonymity in Blockchain?
No Counterparty Risks
Because there are no intermediaries involved in DEX transactions and they rely on smart contracts, the risk of counterparty gets eliminated. To ensure that there are no other risks involved, users can browse the internet to find if the smart contracts of the particular exchange have been audited or not and make their decisions based on the traders’ experiences.
Cons of using a DEX
Despite the advantages mentioned above, there are also some drawbacks to using a DEX. These are as follows:
Technical Knowledge Required
DEXs can only be accessed with crypto wallets that can interact with smart contracts. Thus, users must know how to use these wallets and be clear with the concepts related to the security of the funds.
With complete technical knowledge about withdrawing coins to the right network, traders can go right into many places, saving them from losing their funds.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Blockchains have smart contracts that anyone can review publicly. To err is human, and the code might have some exploitable vulnerabilities. As a result, new potential exploits can arise that can cause funds leakage.
Additional Read: Most Popular Smart Contract Vulnerabilities in Smart Contracts
Unvetted Token Listings
Everyone can list a new token on DEX and pair it with other coins to provide liquidity. This leads to many scams like rug pulls that make the situation hard for investors.
The Bottom Line:
Decentralized exchanges offer an intriguing option, even though centralized exchanges continue to dominate the cryptocurrency market and meet the demands of regular investors and traders.
By connecting buyers and sellers without needing a third party’s trust, DEXs provide new models of equitable participation and governance for all stakeholders. There is a lot of importance of DEX for users.
Some improvements are needed in terms of enhancing user experience, infrastructure, scaling mechanisms, and more connections to centralized crypto. DEX is definitely the future exchange; hence, DEX audit will play an important role in minimizing crypto hacks!
Additional Read: How to Audit Smart Contracts?

