?Polkadot is a scalable, interoperable & secure network protocol for the next web.?
Every blockchain technology is based on three principles: decentralization, scalability, and security. Adhering to these three principles has been a challenge for even the largest blockchain networks to date. Where decentralization is easily achieved by all, ensuring scalability and security becomes a task.
Polkadot is a blockchain protocol that enables different blockchains to run independently within one network, protected by a shared security system.
In this article, let’s take a closer look at Polkadot, its architecture, and what makes it so unlike in character to the other blockchains!
What is Polkadot?
Table of Contents
Led by Gavin Wood, co-founder and former CTO of Ethereum, Polkadot is a next-generation blockchain protocol connecting multiple specialized blockchains into one unified network. It is designed to return control to individuals over internet monopolies., Polkadot thrives on the revolutionary promises of older blockchain networks while offering several other fundamental advantages.
To simplify it further, Polkadot will enable a completely decentralized web where users are in control.
Polkadot is fabricated to connect private and consortium chains, public and permissionless networks, oracles, and future technologies. It brings blockchain interoperability, thereby significantly increasing the scalability, speed, and extensibility of blockchains. Because of this, it promises to aid an internet where, via the Polkadot relay chain, independent blockchains can exchange information and transactions easily.
The Polkadot Architecture
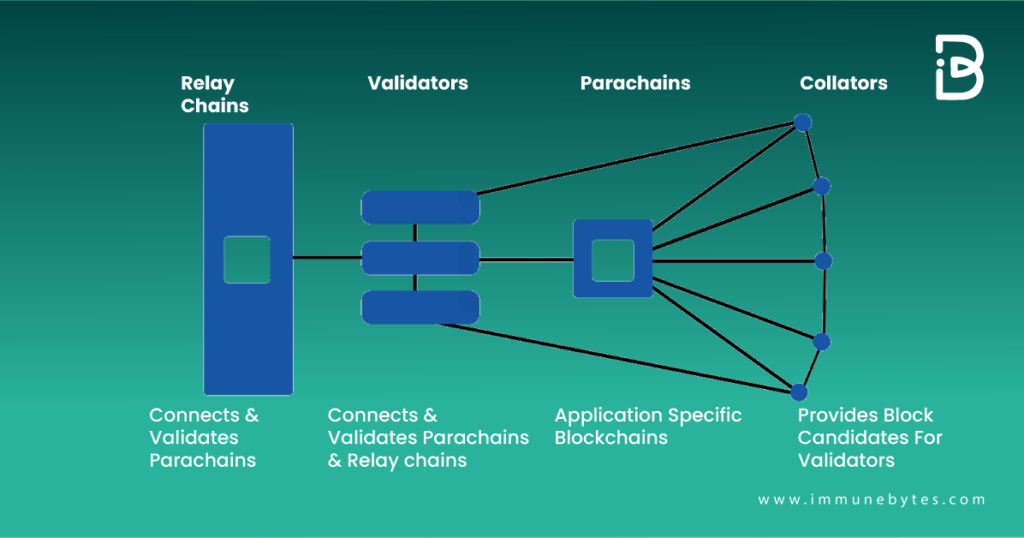
The most common terms one hears when talking about Polkadot are the relay chain, parachains, and part threads. These are building blocks of the interoperability that it claims to offer.
The relay chain is one such mechanism upon which a large number of verifiable data structures can be hosted, called parallelized chains or parachains. Polkadot provides networking and consensus layers that allow developers to focus on creating business logic with unique features and implementing it in a parachain.
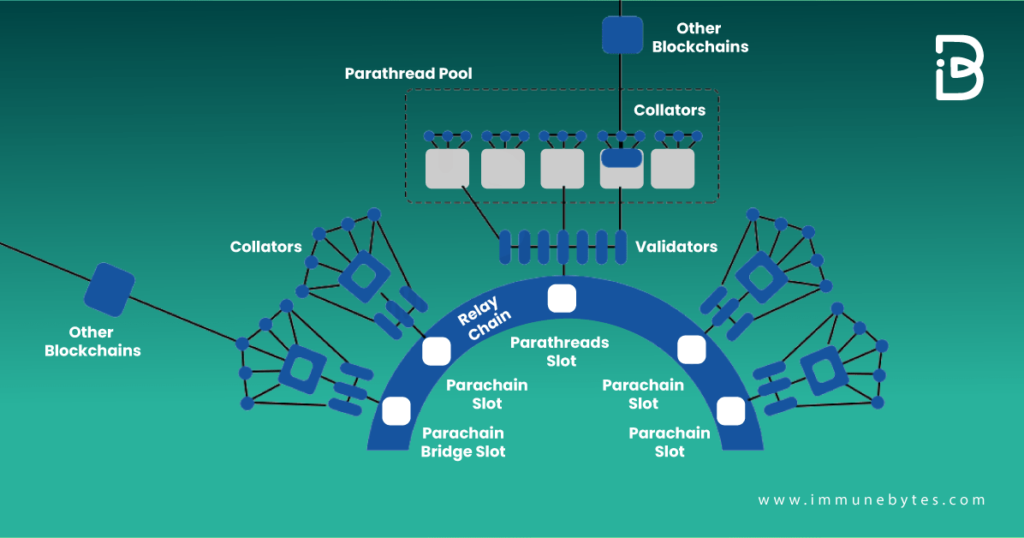
- The Relay Chain
It provides security for sharded blockchains running in parallel (parachains). Transactions from the parachains are confirmed on the Relay Chain using a system of validators.
It is similar to a blockchain like Ethereum in that it is state-based, with states mapping addresses to account information such as balance and number of transactions.
The relay chain acts as the central hub of the Polkadot network, and it
- stores block from all parachains
- is responsible for interchain messages
- ensures security for parachains
- provides a consensus mechanism
Polkadot has implemented flat transaction fees, regardless of the number of transactions, to help avoid scaling issues.
- Parachains
These are customized blockchains that can be run according to their own rules and regulations. The system allows the parachains to interoperate, meaning they can communicate with each other and exchange data or tokens.
Early blockchains had limited throughput and lacked runtime specialization making them impractical to scale for many real-world use cases. Sharding allows transactions to be processed in parallel, increasing throughput.
- Parathreads and Parathread Slots
Parathreads are similar to parachains but only occasionally establish a link to the relay chain, making it possible to have pay-as-you-go security.
Polkadot supports multiple execution slots that work like a computer’s core. Each processor runs one process at a time. Parathreads share these slots amongst a group, making them a part of a pool, termed as a parathread pool, that shares slots and must win auctions for individual blocks.
- Bridges
Bridges serve as a gateway for parachains and parathreads to connect with external blockchain networks such as Ethereum and/or Bitcoin.
- Second layer relay chain
The main technology that allows Polkadot to scale. Each relay chain can carry more parachains and relay chains.
After some time, second-layer relay chains are added to the main chain. Making the Polkadot network appear similar to a tree that connects independent clusters of parachains. This is the main advantage of Polkadot, as such scaling is theoretically unlimited.
Recommended for Polkadot Security Audit
Polkadot’s Consensus Mechanism: NPoS
The Polkadot blockchain will implement Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS), a relatively new type of scheme used to select the validators who are allowed to participate in the consensus protocol. Let’s see how it works.
A couple of times per day, the system selects a group of entities called validators, who, in the next few hours, will play a key role in highly sensitive protocols.
They are also required to stake their DOTs, Polkadot’s native token and their job is demanding as they need to run costly operations, ensure high communication responsiveness, and build a long-term reputation of reliability.
A DOT holder will also be encouraged by the system to participate as a nominator. The nominator publishes a list of validator candidates that they trust and puts down an amount of DOTs at stake to back them.
This nominator-validator arrangement gives strong security guarantees. It allows for the system to select validators with massive amounts of aggregate stake and eliminate candidates with a low stake. Read more about NPoS here.
Polkadot is a rapidly evolving network, and a lot of startups have already chosen it as their foundation for blockchain development. It promises a lot of profit from cross-application interoperability, not to mention the scalability of blockchain development.
The network has been fully decentralized since June 2020, and staking is active. Staking on Polkadot has also started to become popular. Early parachains are currently running on the testnet Rococo. The first parachains are being launched on Kusama, Polkadot’s wild cousin, before moving onto Polkadot.
Final Thoughts
With such features, Polkadot has the potential to become an integral part of the blockchain economy.
Stay tuned for the next part of this blog, wherein we will touch on the technical details of the Polkadot Network and list some of the projects on the network.
About ImmuneBytes
We are a team of India-based security professionals who are skilled in their niche. Although a start-up, you’ll never have to compromise with anything from us. We strive to push forward and provide overall surveillance and quality service to our customers. Get in touch with us to get a security audit for your smart contract.

