What has made blockchain and web3 a revolutionary technology today? The answer lies in its decentralized and trustless architecture.
And this is what public and private keys facilitate. They are a pivotal technology that has allowed users to carry out financial transactions without needing third-party interference to verify them.
Are you someone who wishes to dwell deeper into web3 security? Then, this is surely the blog that is a must-read for you. Here, we will discuss public and private keys, how they work, and all the types of web3 security risks associated with them.
ImmuneBytes is a treasure chest of the answers that you are looking for. We have an erudite panel of cybersecurity professionals who work day and night to provide top-notch smart contract auditing services to clients worldwide and save them from expensive hacking exploits.?
So, what are we waiting for? Let’s get started.
Cryptography
Table of Contents
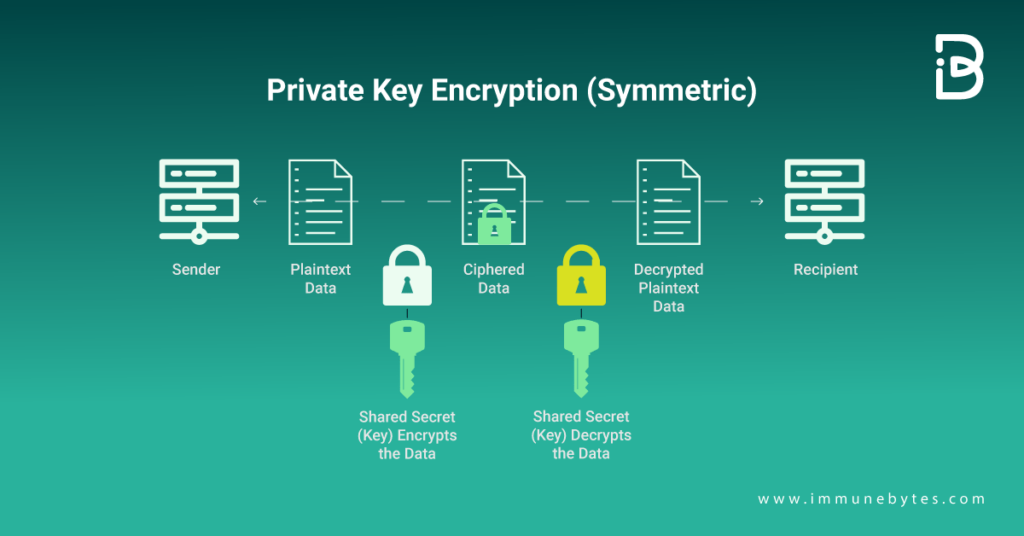
Since the inception of cryptography, private keys have existed in some form. Those were led by academicians and military personnel who wanted to encode messages. They decoded them using a secret phrase. This phrase might encrypt the message first, then decode it. The fact that the same phrase was used to both encrypt and decode the message was a serious flaw in the design, making it possible for an unauthorized individual to both read the contents and pass as the message’s sender if the phrase were hacked.
Because both parties to the earlier encryption process utilized the same word, it is known as “symmetric encryption.” To tackle the issues with the prior art, cryptographers divided the procedure into two halves to produce a “public” and a “private” key in the 1970s.
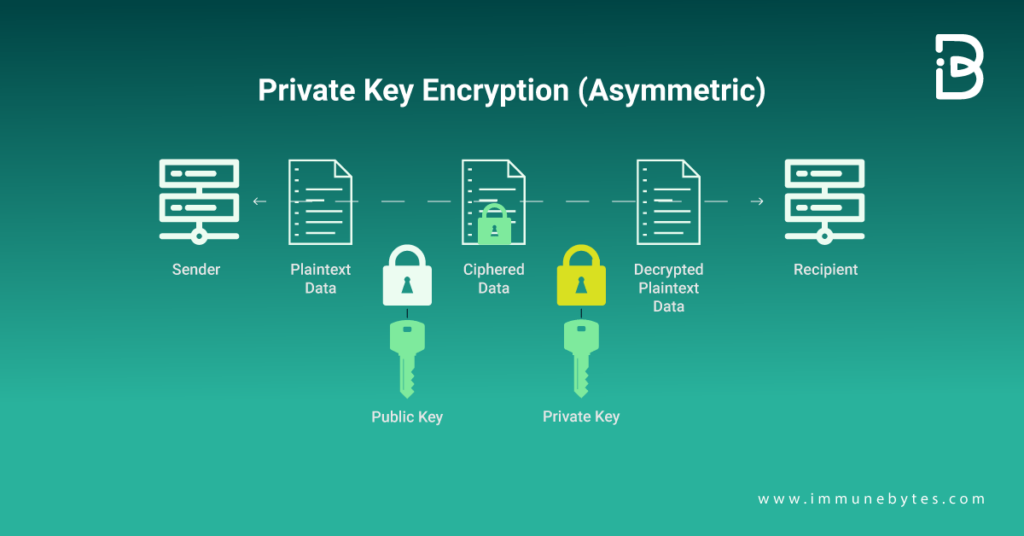
One key technological component that makes cryptocurrencies possible is “Elliptic Curve Cryptography.” the private key in this new approach is a long, random prime integer that may be used as a special ID to encrypt and decode messages. The mathematical operation known as “elliptic curve multiplication” can produce a public key from this private key. Importantly, a private key cannot be converted into a public key and vice versa.
Additional Read: Quantum Computers Will Impact Bitcoin?
Now is the perfect time to go ahead discussing private and public keys.
Private Key V/S Public Key
Let us dive deeper into the world of the private key and public key that has made decentralized transactions possible for users.
Private Key
“Keep the private key private.'”
You might use a debit or credit card with a secret PIN. It is suggested that you don’t share it with anyone as it helps make all the transactions. Also, the people who know the pin can easily access your funds and even empty them! Similar is how the private keys work. If any wrong person gets access to the private key, it will harm you.
Thus, there is a vital importance to keeping a private key ‘private’ for web3 users.
The case of users who store their funds on centralized exchanges and custodial wallets is different; they are solely trusting a third party to keep their funds safe, just like you would trust a bank to safeguard your money.
If you don’t want a third party’s interference in your transactions, then opting for a non-custodial wallet is your best option. However, you must take care of your private key and keep it safe from others. The private keys come in the form of ‘seed phrases.’ It is a sequence of words that will help you encode your private keys.
Whichever method you choose, you will find hackers with prying eyes on your funds. They will target phishing attacks to get sensitive information from the users. Therefore, remember the golden rule: “NEVER SHARE YOUR SEED PHRASE WITH ANYONE.”
What Is The Use Of Private Key Cryptography?
Symmetric encryption, often known as private key encryption, employs smaller keys that are simpler to compute. These still offer sufficient computational hardness, but their usage is less demanding on the client and server. This is crucial, especially at scale, and symmetric encryption’s major benefit.
Public Key
The ability to send money and other assets to an address is made possible via a public key, a lengthy number sequence generated from and matched with a private key. Similar to an address in the physical world, it enables anybody who has it to send a letter at any time. However, in this situation, the letter is sent as a web3 asset, such as a cryptocurrency or NFT.
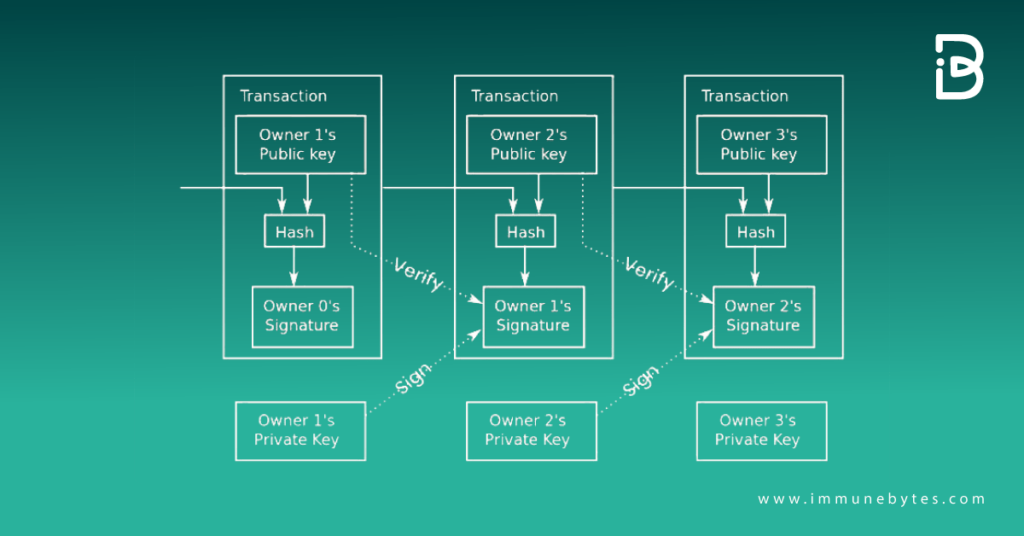
Bitcoin founder Satoshi Nakamoto while designing blockchain transactions, gave details on how public and private keys smoothen the transactions using digital signatures.
The diagram below shows the process mentioned in the Bitcoin whitepaper.
Uses of Public Key Cryptography
There are two main uses of public cryptography, which are as follows:
- Authentication
- Key Exchange
Both of these actions take place during the handshake. They perform crucial roles. It is more difficult to control these functions using a big key. Although still very secure, the key’s size can be decreased to improve performance. Once public key cryptography is complete, the two parties have exchanged keys and established their identities. Now all that remains is for us to communicate truly.
Too overwhelming? Well, we have just the perfect solution for you. Let us simplify it for you. Below we have enlisted the difference between public and private keys in a tabular form for a better understanding.
| Private Key Cryptography | Public Key Cryptography |
| It is faster than the public key. | It is slower than the private key. |
| The secret key and algorithm are used to encrypt and decrypt the message. | Two keys are used- one is used for encryption, while the other is used for decryption. |
| The key is kept as a secret. | One of the two keys is kept as a secret. |
| It is known as symmetrical, as only one key is the secret key. | It is asymmetrical because two types of keys are used. |
| Senders and receivers need to share the same key. | It is not necessary for the senders and the receivers to share the same key. |
| The key is private. | The public key can be public, and the private key is private. |
Understood? Even if there are doubts regarding public and private keys in cryptography, we are all ears to your queries. Get in touch with us, and we promise not to leave a stone unturned for you.
Final Thoughts
Due to this transparency, there have been a lot of web3 security solutions and blockchain analytics platforms that assist projects in monitoring behavior on-chain. This is crucial for web3 security because, in the case of a hack, it is important to understand what circumstances led to the assault, where the stolen funds went, and what can be done to minimize the effects.
Public keys’ transparency benefits web3 security, giving hackers a great tool for scouting possible targets. It is feasible for a new address to be formed every time a person makes or receives a transaction, given how public keys are created from private keys. This, in turn, aids users with web3 security’s privacy feature.
One of the important concepts for comprehending the web3 environment is the interaction between private and public keys. Understanding their operation helps comprehend a variety of web3 technologies that follow, as well as the consequences for web3 security.
Two things are crucial to keeping in mind while looking for doable solutions to preserve security around their public and private keys. First, never divulge your private key to a third party, as this gives them access to your money and other valuables. Second, decide whether you want to keep control of your private keys or entrust a custodial wallet with that duty. Be sure to carefully consider both before choosing because each has benefits and drawbacks.
Fear not, ImmuneBytes is your Web3 security partner, and we will do everything to make financial transactions safer for you within the Web3 space!

