After the development of Ethereum as an ideal destination for smart contract deployment, many crypto-enthusiasts started exploring opportunities to delve into blockchain applications.
2017 specifically saw a massive increase in the number of decentralized applications, highlighting the significance of mainnet and testnet separately.
This blog will talk in detail about the mainnet, and testnet, their differences, use cases, and working mechanisms.

What is a Mainnet in Blockchain?
Table of Contents
Mainnet is a completely developed, fully functional blockchain network. Signifying that it records, broadcasts, and verifies the transactions committed on a mainnet on the distributed ledger.
Mainnet executes the actual transactions within the blockchain network and records them for public usage.
The main net’s deployment shows the developers’ confidence in the capabilities of their blockchain. For instance, the open-source blockchain platforms Ethereum and Bitcoin carry out genuine transactions with real financial value in the mainnet setting and are publicly verifiable.
Examples of a Few Well-Known Mainnets:
- Ethereum mainnet
- Polygon mainnet
- BS mainnet
- Aurora mainnet
- Tezo mainnet and many more.
Why is Mainnet Important in Blockchain?
Mainnet is the actual platform where users interact and transact with the crypto native to the protocol in question.
For instance, the Ethereum mainnet is the only public network of the Ethereum network where applications are interoperable, leveraging the potential of the decentralized world.

Credibility
Without the mainnet, a blockchain project is merely a concept rather than an actual working entity for having any use case.
The main network is the actual functioning blockchain protocol where participants can exchange native blockchain currency for conducting transactions with one another because all transactions are live.
The presence of a mainnet permits the formation of a live ecosystem of users, allowing for real-time interaction and transactions to take place in complete transparency.
Verifiable Proof of Development
Deployment on the mainnet is verifiable proof that a project has a functional blockchain, where real-world transactions are taking place transparently.
The existence of a mainnet indicates that the project is active and making advancements. A live mainnet would also put the blockchain’s functionality and capacities to the test because anyone can participate in the network, and any errors could jeopardize the blockchain’s internal operations. In order to make sure that every component is operating as it should, it takes a lot of resources and development to launch the mainnet.
Actual Transactions Occur on The Mainnet
As discussed above, the mainnet is where the actual transactions occur.
It is a fully functional blockchain platform that enables users to send and receive cryptocurrency transactions and any other kind of digital data stored on a distributed ledger.
How Does Mainnet Work?
A mainnet is a separate blockchain that operates on its own network using its own protocol and technologies? a live platform using cryptocurrencies and tokens to perform transactions.
Working of a Mainnet:
Working on the mainnet is determined by the consensus mechanism used for the particular network.
For instance, blockchain networks that use Proof-of-Work allow miners to validate these transactions and earn block rewards.
On the other hand, stakers confirm transactions on Proof-of-Stake blockchain mainnets based on their network stake and receive the transaction fees users pay.
Transactions on the mainnet use the network’s native crypto and tokens, and the distributed ledger keeps their track.
Use Cases of Mainnet
- After the launch of the mainnet, most blockchain networks open-source the underlying code, building trust amongst the crypto-community.
- Anti-spamming and other safety measures of the blockchain adjoins the projects deployed on the mainnet.
- Mainnet demonstrates the functionality of the blockchain. It gives an open welcome to everyone to sign up for the network.
- More decentralized applications (dApps) can join the blockchain thanks to the mainnet application’s use cases.
- Mainnets are fully functional blockchains used to send and receive any transaction, including information transfers and payments made in the form of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) or cryptocurrencies.
Additional Resource: BNB Testnet Faucet
What is Testnet in Blockchain?
Testnet is the simulation or the working prototype of the mainnet ecosystem. It is an alternative environment to the actual blockchain mainnet functionality, where testers, developers, and blockchain security audit professionals can trial-run their projects.?
Testnet is not a wholly developed blockchain and is majorly used for the troubleshooting aspects of a smart project.
Testnet assists in fixing bugs and other network failures that could harm the functioning of the project at a later stage.
Following are the Examples Of Testnets:
- Sapolia
- Kiln
- Goerli
- Polyscan
Why is Testnet Important in Blockchain?
The testnet phase, which serves as the trial run before the official launch, is crucial.
Imagine sending millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency without first verifying that the Blockchain worked as intended and then losing all of it. Developers naturally want to prevent it from ever happening, which is why the testnet phase serves as a protection.
Dynamic Development
Blockchain is still in its initial stages of development; hence, frequent testing and error analyses are the need of the hour.
For instance, EIP 1559, the famous hard-fork update on the Ethereum network, has gone through a number of trial and error runs on the Ethereum testnet before being deployed on the mainnet.
Recommended: Blockchain Security Audit Firm
Prevents Disruption
A testnet enables protocol testers, application developers, and even security personnel to test the protocol’s features and functionalities in a separate setting without worrying about interfering with the main Blockchain.
No Cost Trial
Mainnet processes the actual transactions, where tokens have a backend value, but in the case of a testnet, tokens do not have any value attached to them.
Testnets offer a testing area for developers eager to build blockchain applications or test out specific capabilities without investing real money. Testing application features or performing research on the mainnet would be pretty expensive for developers.
How Does Testnet Work?
Testnet is basically a simulation environment for the mainnet and works exactly like the mainnet. The difference lies at the core, where the testnet is just a trial and the mainnet is the real-world entity. Transactions happening at the testnet do not have an intrinsic value, unlike the mainnet.
Use Cases of Testnet
- Projects released on the Blockchain for public participation can be tested in a testnet to avoid bugs.
- On a testnet, tokens have no value, while using actual money on the main network results in higher operating costs.
- The low transaction frequency of a testnet makes it simpler for programmers and testers.
Mainnet Vs Testnet: Which one is Better?
If the mainnet is the real-world entity, the testnet is the laboratory for experimenting with the working of blockchain projects before deploying them on the mainnet.
It is not about whether the mainnet is better than the testnet or vice-versa, it’s about the application you are looking for.
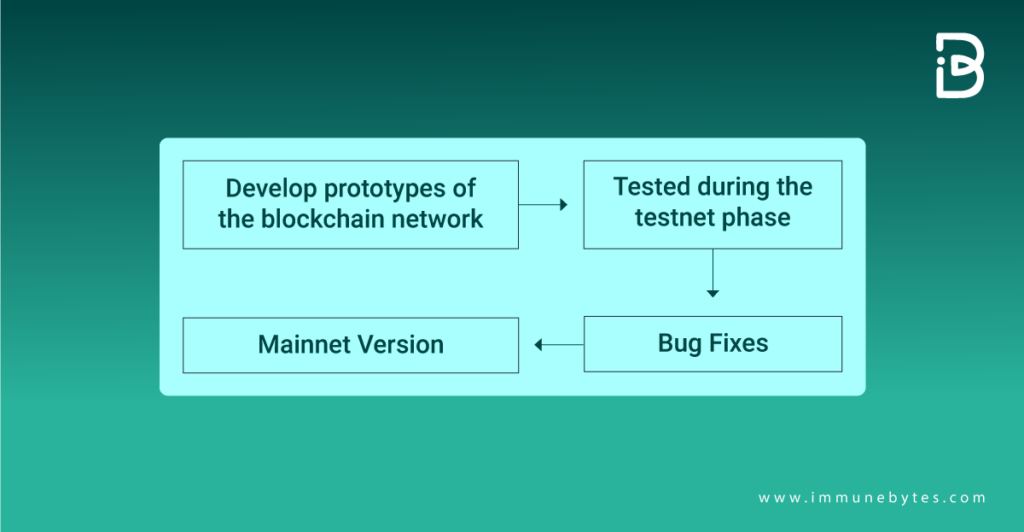
Fig: Stages of blockchain application development.
Testnet is preferable at the developmental stage, while mainnet use begins once the project development is in its completion stage.
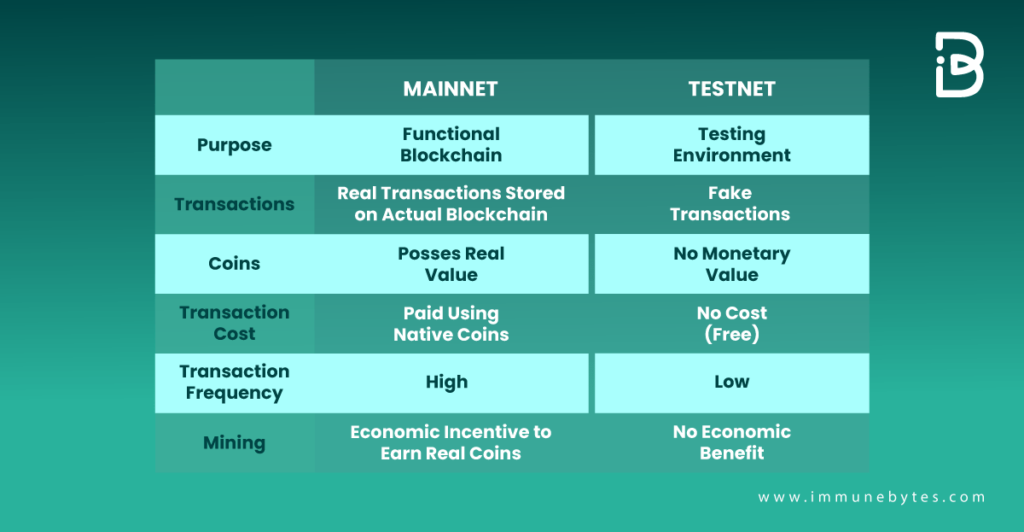
Here is a Table Showing the Difference Between the Two
Wrapping Up
Although blockchain protocols use and refer to several settings or stages, the testnet and mainnet descriptors accurately encapsulate the primary development stages of most protocols.
Hence, it is imperative to understand their key differences and the stage of their deployment.

