Penetration testing is a preventive strategy that consists of a series of legitimate tools to identify and exploit a company’s security flaws. It employs similar techniques as malignant hackers to exploit critical vulnerabilities in the company’s security system. Penetration testing is more like “cracking the lock” rather than just “accessing the lock.”

These analyses indicate how easily a hacker can breach an organization’s security controls and allow access to its sensitive and confidential information assets.
This blog will talk about two forms of pentesting, i.e. Internal and external penetration testing. Alongside this, it includes the examples and tools used to conduct these tests.
External Penetration Test Explained
Table of Contents
External network penetration testing is a limited, simulated hacking technique. It entails a security professional attempting to violate your system via an external network in order to expose the magnitude of your project’s security vulnerabilities.
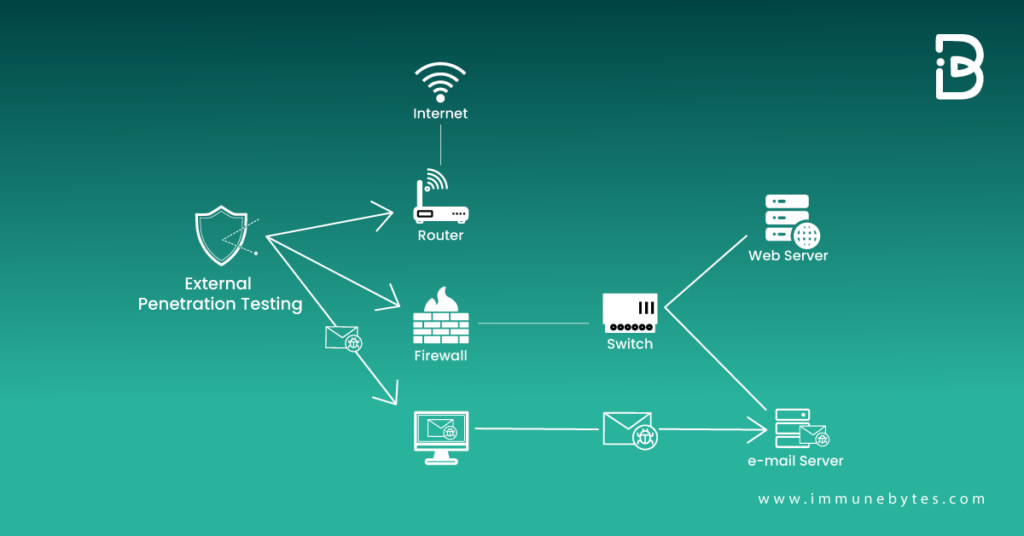
Must Read: External Penetration Testing
Internal Penetration Test Explained
Internal network penetration testing is the process of exploiting your own system from the insider’s perspective. The goal, in this case, is to protect the system from an attacker who already has initial access to the system.
It can assist testers in determining how much damage a malicious employee could cause if they attack or spread malware.
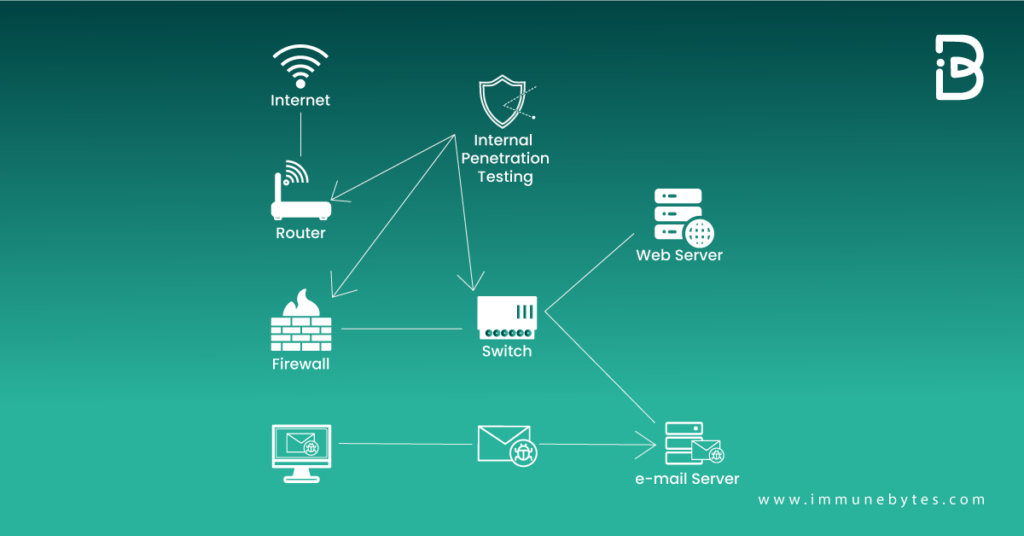
Must Read: Internal Penetration Testing
Examples Of External and Internal Pentests
Internal and external pentests differ concerning the attacking types they test for. Internal pentests look for bugs that could be exploited by malicious employees or business partners within the organization. In contrast, external pentests analyze security vulnerabilities from outside the system.
Examples of External Penetration Test
- Error control test
- Configuration & Deployment Management Test
- Authentication Test
- Identity Regulating Test
- Authorization Test
- Input validating test
- Cryptography test for weakness
- Intended business behavior Test
- Client Side Test
Examples of Internal Penetration Test
Internal penetration testing involves triggering the following points of internal errors.
- Computers, workstations, and portable devices
- Points of entry
- Servers
- HVAC systems with internet access
- Wireless networks
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
- Firewalls
Penetration Testing Methodologies
Penetration Testing methodologies depend on the types of vulnerabilities you are looking for.
External Penetration Test Methodologies
- IDS/IPS Testing
- Scrutinizing for public information and information leakages.
- Manual testing identified vulnerabilities.
- Footprinting
- Password Strength Test
- Data breach test
Internal Penetration Test Methodologies
- Internal Network Scan
- Port Scan and Fingerprinting
- Manual Vulnerability Testing and Verification
- Firewall and ACL Testing
- Password Strength Test
- Network Security Controls Test
- Database Security Controls Test
- Internal Network Scan, Trojan test
- Privileges Escalation Testing
Popular Tools of Penetration Testing
Testing tools for internal and external penetration tests are standard, depending on the entities they are applied to look and exploit for vulnerabilities.

Following are penetration testing tools popularly deployed by pen-testers.
- Burp Suite Pro
- Wireshark
- Nikto
- Sqlmap
- Nessus
- Archini
- Metasploit Framework
- Nmap
- Custom Scripts
- Hydra
- GHDB
- Openvas
Recommended: Penetesting Services Company
Mapping Up: Difference between Internal and External Pentesting.
In order to understand the pros and cons of both testing techniques, look at the table differentiating between the two.
| External Penetration Test | Internal Penetration Test |
| Identify vulnerabilities from an external attacker’s viewpoint. | Identify vulnerabilities from an internal attacker’s viewpoint. |
| Outsourcing testing is cost-effective as it does not require maintaining a team of security professionals. | Requires an in-house security team to be maintained. Hence, expensive. |
| Requires planning before and is often done a few times only. | Provides a regular way of ensuring security. |
| Less comprehensive as testing is done only to prevent an external threat. | It can be more comprehensive because an authorized user can hack into an organization’s information system using either an internal or external system. |