Together with the business sector, even the other sectors like food services, manufacturing, finance, government, healthcare, etc., remain in blockchain use cases. Smart contract vulnerability becomes common owing to the immutable nature of smart contracts, making them even more susceptible to phishing attacks.
Blockchain has evolved at a breakneck pace?within the business domain, users have adopted it due to its utility in digital identity verification and safer transactions through smart contracts.
With the adoption and increased surge of Blockchain and Web3 technologies, Microsoft has warned everyone of new cyber threats like ?ice phishing? that have left the so-called secure De-Fi space at the mercy of hackers. They have discovered attacks resembling classic credential phishing attempts on web2, but others are unique to web3.
You might have heard about phishing; however, ?Ice phishing? is a relatively newer concept. This blog will give you a complete understanding of what is an ice phishing attack, how it works, examples, and how to prevent such attacks.
Let’s get started.
What is Ice Phishing Blockchain Attack?
Table of Contents
If Blockchain and Web3 are considered secure environments, how can phishing attacks wreak havoc within this space? The answer is social engineering.
Following the December 2021 Badger DAO blockchain breach, in which the attacker stole $121 million from 200 accounts, Microsoft has warned that ice phishing may be the next fad among attackers. It can put your Bitcoin in jeopardy. As a result, it is critical to be aware of such dangers and exercise caution to secure your crypto wallet information’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Attackers are as intelligent as they are wicked. According to Microsoft security specialists, the attackers are obtaining a malicious smart contract signed by unwary users, redirecting tokens from non-custodial wallets to an attacker-controlled address rather than their own. It is difficult to identify or trace token displacement in Web3 due to the need for more transparency on the transactional interface.
Doesn’t it sound familiar? This seems similar to the phishing emails that hackers send to defraud companies. However, this is ‘ice phishing.’
Deceptive activities lure users into signing transactions that allow cyber attackers to utilize tokens. Delegating token usage permission is a prevalent form of smart contract transaction, particularly in DeFi.
An “ice phishing” attack involves a malicious hacker modifying the contract spender’s address? switching it over to the attacker’s address. The primary reason why this technique is effective is that the existing user interfaces do not show all relevant information that might indicate contract tampering.
After signing the ice phishing contract/approval, the attackers get access to any corresponding financial resources. Current ice phishers often gather permissions over time before draining all money resources.
Now, let us see how this attack works.
How Do Ice Phishing Attacks Work?
Undoubtedly, the credential hacks in Web2 are extremely similar to the cryptographic key exposure in Web3. Just like malicious actors trick users into sharing their credentials in the Web2 space, they use similar tactics to trick users into revealing their cryptographic keys.
The ice phishing blockchain attack on the Badger DAO network in December 2021 could not be stopped, and the attacker stole $121 million in Bitcoin from 200 accounts. Unlike other phishing attacks, the ice phishing hack employs a complex methodology. A cryptographic key is associated with your blockchain account that comes with a non-custodial wallet. This key serves as your signature, authorizing transactions from your account. If the attacker has access to this key, they may be able to steal your cryptocurrency.
As soon as the users reveal their keys to an illegal partaker, the attackers gain access to their funds.
Let us understand how an Ice phishing attack works with the help of this graphic below.
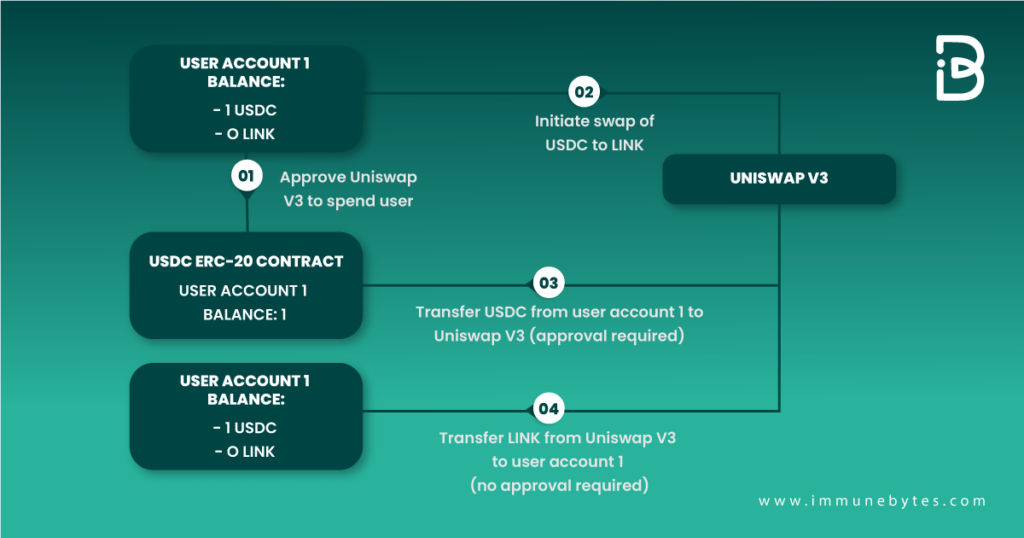
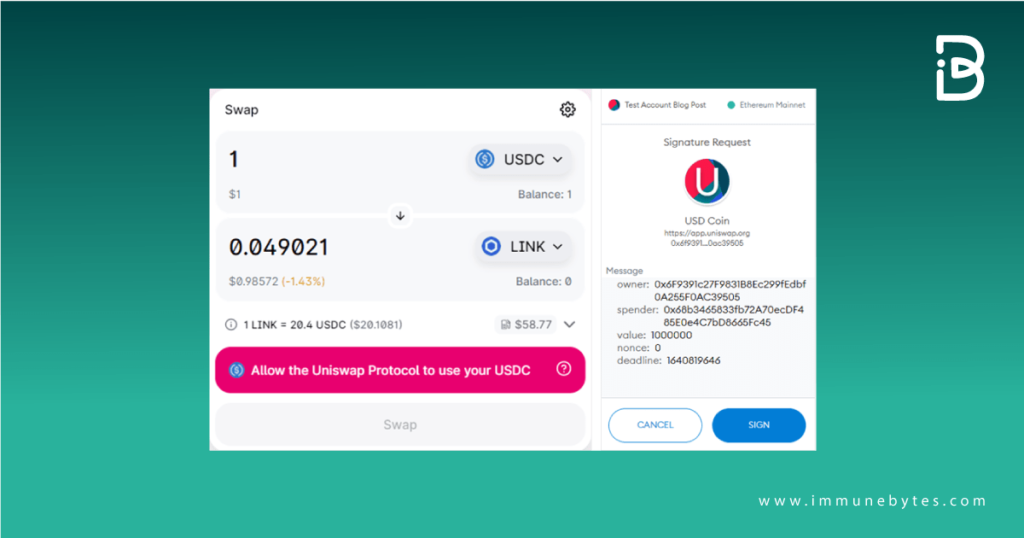
Attackers will pretend to be a customer representative for a crypto service and approach the users to help in any project. The next step will be to hook them into signing a transaction that allows them to get approval for the users’ assets to be moved to the attacker’s control.
This holds most effective for DeFi services like DEXs because they are complicated to understand for novice users and require a MetaMask connection. Users will get a fraudulent link purporting to be a DEX, and when the users sign the transaction, the attacker will alter the sender’s address to his address.
MetaMask doesn’t show an identifiable name but the contract hash. Naturally, such a move would only be evident once you ran the contract address via a block explorer or blockchain analytics tool to ensure it is for the entity you anticipate rather than the attacker.
An Example Of An Ice Phishing Attack
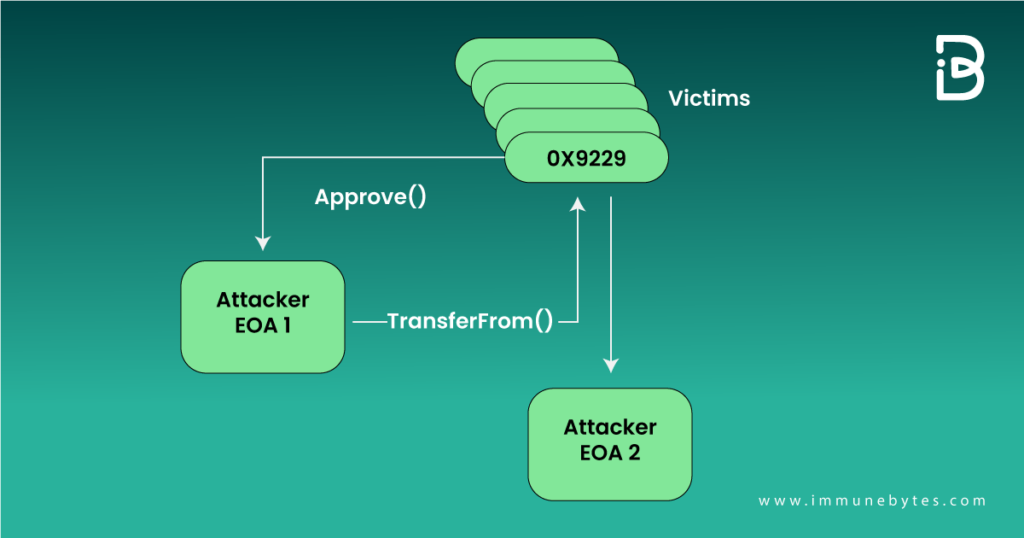
On 17th December 2022, hackers stole 14 Bored Apes (NFTs) from the expensive and famous Bored Apes Yacht Club (BAYC) collection. An investor was persuaded to sign a transaction request masquerading as a film contract, allowing the scammer to sell all of the user’s apes to themselves for a pittance.
The flow of this attack is shown below.
Another Popular Ice Phishing Real World Example: The Badger DAO Attack
Badger is a DeFi protocol that allows one to earn interest on Bitcoin deposits; it launched on Ethereum mainnet in December 2020. Users deposit wrapped Bitcoin into vaults that earn yield through a variety of yield farming strategies. Badger currently has 978 million US dollars total volume locked (TVL).
Badger smart contract front-end infrastructure (in particular, its Cloudflare portion) was compromised (gaining access to a Cloudflare API key), allowing the attacker to inject malicious script into the Badger smart contract front end. This script requested users to sign transactions granting ERC-20 approvals to the attacker’s account (0x1fcdb04d0c5364fbd92c73ca8af9baa72c269107).
The script was first injected into app.Badger.com on November 10, 2021, but injection was inconsistent, only targeting wallets with certain balance and modifying the script periodically. Injection stopped on December 2, 2021 at 12:31:37 AM (UTC).
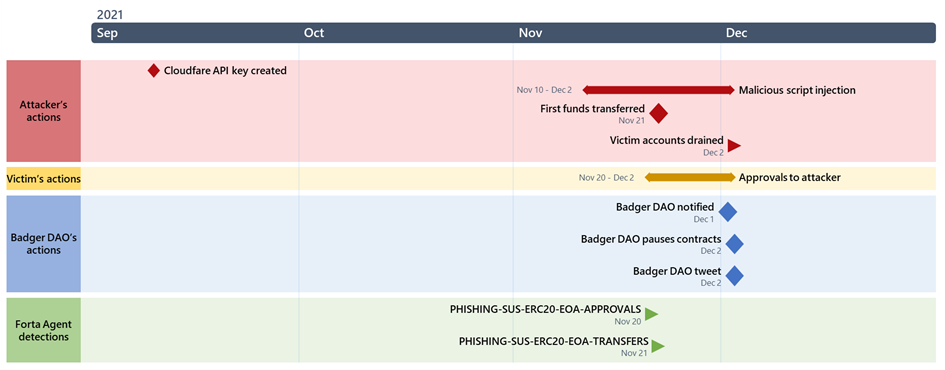
On November 21, 2021, the first funds were transferred by the attacker (possibly a test transaction). On December 2, 2021 at 12:48:25 AM, actual funds were drained from victims’ accounts.
This draining of funds continued until 10:35:37 AM that day. Badger paused contracts (where possible) starting at 03:14:00 AM, causing some of the attacker’s transactions to fail. In the end, the attacker was able to drain 121 million US dollars from almost 200 accounts within 10 hours.
How To Avoid Not Getting Hooked By Ice Phishing Scammers?
Now that you know the problem and how it works, it becomes crucial to understand how to prevent ice phishing blockchain attacks.
These are some of the ways through which we can prevent these attacks.
- Ensure the address on your smart contract is correct. For this, you need to monitor the front-end appearance of the contract regularly. Also, check how the contract address looks elsewhere on the transaction.?
- Go for smart contract auditing.
- Check if your smart contracts have incident response buttons such as pause/unpause?
- When signing a transaction in Metamask or any other wallet, it is critical to examine the transaction details and guarantee that it will begin the actions you want.
- Keep long-term holdings, such as more value NFTs, in cold storage, cash for transactions, and more active dApps in a separate hot wallet.
- When sending payments or granting access to crypto assets in your account, check the contract hash in Etherscan or with a blockchain analytics tool to guarantee it’s the entity you’re looking for.
- Always interact with legitimate corporate employees and be suspicious of anybody who claims to be a customer support assistant on social media, Discord, or other platforms. When in doubt, verify with the project via officially recognized email and social media channels.
- Always visit dApps and services through the confirmed URL to avoid phishing URLs and domain squatters. If in doubt, check their verified Twitter account for the project URL.
- Manage your crypto currencies and tokens through multiple wallets and/or periodically review and revoke token allowances. https://etherscan.io/tokenapprovalchecker makes doing this easy.
Keep Your Cryptos Safe!
As the value and usage of cryptocurrencies continue to rise, ice phishing and other crypto scams are expected to become more widespread. Users should understand how these schemes operate so that they may take the required precautions to protect themselves.
These aren’t the only ways scammers use cryptocurrency, but they do show the many strategies used by hackers. These risks are widespread, but with the proper information and procedures, users may prevent them.
ImmuneBytes is a perfect paradise for you if you’re looking for useful information about the Web3 space.