In the last couple of years, blockchain technology aka Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) has grown rapidly. Along with the world?s growing interest in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, there has been a slight glimmer in public interest towards developments in the digital world.
Since blockchain is a decentralized network without any focal authority, have you ever thought about who takes landmark decisions in such a network? Or which transactions are legitimate and should be added to the ledger?
A blockchain achieves all of this using various Consensus Mechanisms.
What are consensus mechanisms?
Table of Contents
One of the most important aspects of a blockchain network, consensus mechanisms are protocols that aim at ensuring that all participants are synchronized with one another and agree on which transactions are legitimate and are added to the blockchain, making sure that each of them disposes of identical copies of the distributed database files.
More simply, a consensus mechanism is a way of reaching an agreement in a group, such that the whole group benefits from it. Without a good consensus mechanism, the blockchain is always at the risk of being attacked.
There are multiple ways to reach a consensus. In this article, we?ve compiled some of the most popularly used ones.
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof-of-Work is the original consensus mechanism in a Blockchain network.
With PoW, miners compete against each other to solve a mathematical puzzle on the network and get rewarded, they provide the computing power required to sustain the blockchain and verify transactions as well as ensure the network?s immunity against hacks. The first miner to solve the mathematical puzzle gets rewarded. However, this whole mining mechanism of bitcoin needs high energy consumption and longer processing time, thereby making it an expensive option.
Mathematical puzzle, what are you talking about?
This is exactly what requires so much computational power. It can be anything from hash functions to integer factorization or even guided tour puzzle protocols. The output of this mathematical puzzle is called a hash.
As the blockchain network grows, so does the consumption of energy needed to fuel the algorithm. Consequently, making the complexity of the task a concern. The main drawbacks include:
- high expenditures
- ?uselessness? of computations
- 51 percent attack.
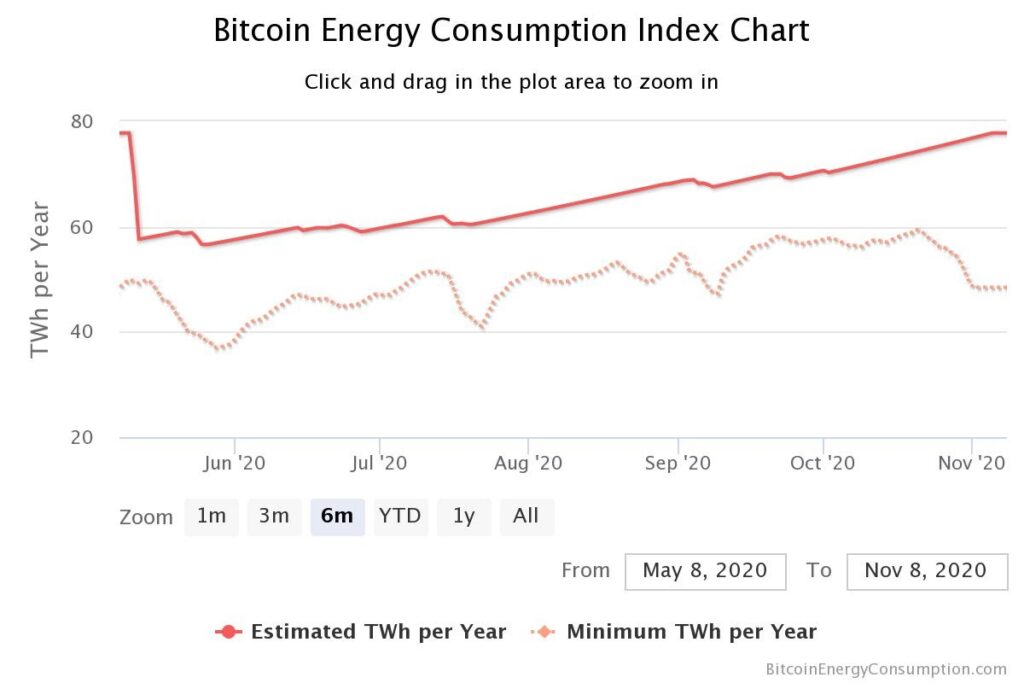
Source: Digiconomist
PoW is the first consensus protocol to be developed and Bitcoin was the first to use it. Another big example that uses PoW is Ethereum. Given that almost every three of four projects are implemented on the Ethereum platform, it?s safe to say that the PoW consensus model is adopted by the majority of blockchain applications
Proof of Stake (PoS)
To combat the high energy consumption problem of PoW, came the PoS, the more environment-friendly brother of PoW. It was first introduced in a paper by Sunny King and Scott Nadal in 2012, wherein they suggested an alternative method called ?staking? which allowed a deterministic algorithm to choose the nodes based on the number of coins they owned.
The basic idea was to separate the voting power of a miner from its computational power based on the percentage of tokens held by them. The larger the share of tokens held, the more likely they are to be selected to mine the next block. The validators or the miners are also rewarded if their block is selected. The reward that they receive for creating the next block depends on the design scheme of the blockchain network they?re in.
Another major distinction is that the PoS ensures that the miners mining the blocks are legitimately interested in the network and are not doing it just for the sake of maximizing their own profit. For carrying out an attack on the network, the miner would need to own at least 51% of the cryptocurrency i.e. the majority of the shares. And no one in their right mind would sabotage the network in which they hold major shares as, if the value of that particular cryptocurrency falls, the value of his holdings would also fall.
As PoS needs neither some specific hardware nor it consumes any energy, it is one of the least expensive blockchain consensus conventions.
Proof of Capacity (PoC)
PoC allows miners to use their available hard disk space to decide their mining rights and validate transactions. It makes use of a process called ?plotting?. With PoC, solutions to mathematical puzzles are pre-stored in the miners? hard drive, whoever is the first to find the solution to the puzzle is the one to create a new block.
Plotting is a term used for allocating storage space to be used for calculations in the Blockchain network. A Plot is a file holding pre-computed hashes that can be used to forge blocks. These are then later used by miners and can be thought of as the miner?s hash rate.
There are certain other consensus algorithms as well such as Proof of Identity (PoI), Proof of Elapsed Time(PoET), Delegated Proof of Stake(DPoS) but those aren?t as widely used.
However, now that we have discussed these mechanisms, the question that arises is, among these widely popular consensus mechanisms, which one is the best? And more importantly, which one should you be using? To know the answers to these questions, stay tuned for our next article.
ImmuneBytes is a leading venture, with a team of security professionals on board who have secured over 175+ projects in different blockchain frameworks and are happy to help you with your smart contract audit, keeping it safe and sound from malicious hackers. Connect with our team today to get your audit.

