Bitcoin is growing, undoubtedly. But the largest cryptocurrency in the world is struggling for mass adoption. Though the attention to Bitcoin increased considerably in 2021, it still has a very long way to go before gaining mainstream traction.
2021 was a notable year in the history of Bitcoin as El Salvador became the first country in the world to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender. But the hustle doesn’t stop. Behind the scenes, a lot of game-changing work is being done as well, such as developers working day and night to make Bitcoin a better payment system.
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network may be its inkling shot at mass adoption. Due to Bitcoin’s high fees & low transaction speed, it is still struggling to be accepted as a widely-used payment method. The Bitcoin network handles 7 transactions/second as compared to your Visa credit card which handles 65000 transactions/second.
Can Bitcoin’s Lightning Network solve this problem? What is Lightning Network and how does it work? Let’s find out in today’s blog!
History of Lightning Network
Table of Contents
The Lightning Network was proposed in 2015 by two researchers, Thaddeus Dryja and Joseph Poon, in a paper titled ?The Bitcoin Lightning Network.? Their writings were based on previous discussions of payment channels made by Satoshi Nakamoto, the anonymous creator of Bitcoin.
The paper’s abstract describes an off-chain protocol made up of payment channels. Dryja and Poon then detailed that Visa peaked at 47,000 TPS. For Bitcoin to come anywhere close to Visa’s TPS, it would have to manage eight gigabytes worth of transactions per block, which is nowhere near the capabilities of the current blockchain.
In 2016, Dryja and Poon founded Lightning Labs, a company dedicated to developing the Lightning Network. Lightning Labs worked to make the protocol compatible with the core Bitcoin network. A breakthrough became possible after Bitcoin’s SegWit-based soft fork in 2017, which freed up space for more transactions to fit in each block and removed a longstanding Bitcoin bug called transaction malleability.
In 2018, Lightning Labs finally launched a beta version of its Lightning Network implementation into the Bitcoin mainnet. At this time, public figures like Twitter founder Jack Dorsey began their involvement with the project.
What is the Lightning Network?

By definition, the lightning network is a second-layer technology applied to Bitcoin that uses micropayment channels to scale its blockchain’s capability to conduct transactions more efficiently. Transactions conducted on lightning networks are faster, less costly, and more readily confirmed than those conducted directly on the Bitcoin blockchain
The network takes the transactions away from the main blockchain and makes them off-chain, henceforth de-congesting the Bitcoin blockchain and reducing associated transaction fees.
In order to be accepted as a mode of payment for the masses, Bitcoin will need to reach tens or hundreds of thousands of transactions per second, similar to credit cards or electronic payments networks. Due to the nature of its decentralized technology that requires consensus from all nodes within its network, Bitcoin is laden with such problems in its current state.
Let’s take a look at how the lightning network aims to solve this problem.
How the Lightning Network Works
The lightning network proposed to solve the scaling problem by creating a second layer on Bitcoin’s main blockchain. This second layer consists of multiple payment channels between parties or Bitcoin users.
A lightning network channel is a transaction mechanism between two parties. Using channels, the parties can make or receive payments from each other.
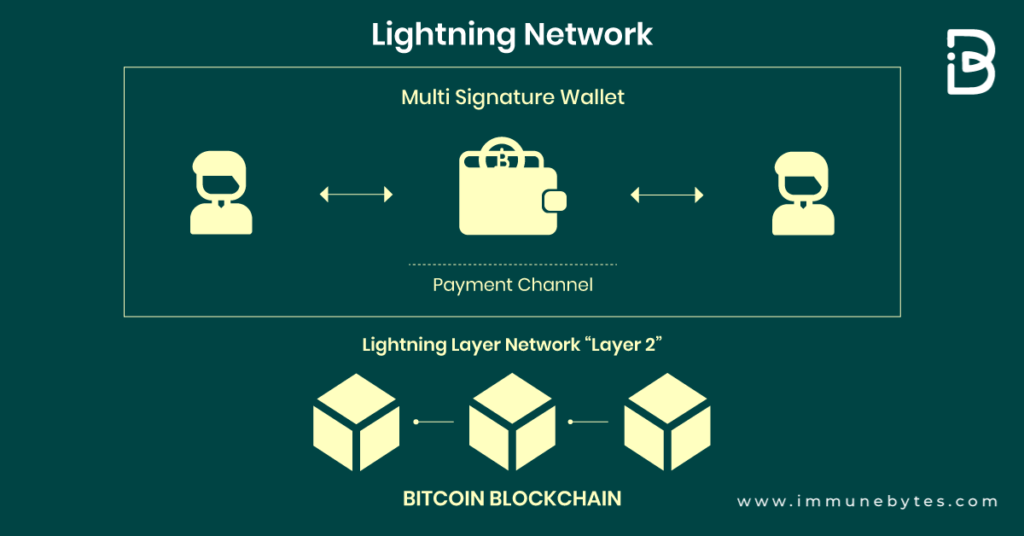
These transactions are processed differently compared to standard transactions occurring on Bitcoin’s blockchain. They are only updated on the main blockchain when two parties open and close a channel. Between those two acts, the parties can shift funds between themselves endlessly without informing the main blockchain about their activities.
Using this approach dramatically speeds up a transaction’s speed because all transactions are not required to be approved by all nodes within a blockchain. Individual payment channels between various parties combine to form a network of lightning nodes that can route transactions among themselves. The interconnections between various payment channels result in the Lightning Network.
Problems Faced by the Lightning Network
Possible Hub-and-Spoke Model
The most obvious problem with lightning networks, which are meant to be decentralized, is that they could lead to a replication of the hub-and-spoke model that characterizes today’s financial systems.
In the current traditional model, banks and financial institutions are the main intermediaries through which all transactions take place. By having more open connections with others, lightning nodes for prominent businesses may become similar hubs or centralized nodes in the network. A failure at one such hub could easily crash a significant portion of (or the entire) network.
Transaction Fee
Another significant problem is the necessity to increase fees to make maintaining the network economically viable. This is true not only for the nodes maintaining the lightning network itself but also for the knock-on cost of potentially higher Bitcoin fees that are translated to the network.
Specifically, there are two parts to their costs. The first part consists of a fee equivalent to Bitcoin’s transaction charges in order to open and close channels between parties. And there is also a separate routing fee to transfer payments between channels.
Since the fees for the lightning network are quite low, in theory, it should attract more participants. However, if the fees are so low for the routing of payments between nodes, there might not be any incentive for the nodes to facilitate the payments. This stands as one of the problems faced by the network.
Malicious Attacks
Another risk to the network is congestion caused by a malicious attack. If the payment channels become congested, and there’s a malicious hack or attack, the participants may not be able to get their money back fast enough due to the congestion.
“Forced expiration of many transactions may be the greatest systemic risk when using the Lightning Network.”, says Dryja in the Bitcoin Lightning Network Whitepaper
Bitcoin’s Price Fluctuations
The increase in Bitcoin’s transaction volumes is largely attributed to a rise in trading volumes. In other words, Bitcoin’s popularity is a double-edged sword since the increased attention garners investment but also attracts more traders increasing the volatility or price fluctuations in the cryptocurrency.
The price volatility makes it challenging for companies to use Bitcoin as a method of payment when pricing their products to sell to their customers or to purchase inventory from their suppliers.
With this, we?d also like to share the considerable number of advancements that have been made to the Lightning Network!
How the Lightning Network Advanced in 2022
With the continuous efforts of the developers at Lightning Labs, the network is swelling in use to make payments more secure and private. Though not an exhaustive list, it highlights a few key advancements made to the network in the previous year.
Bitcoin’s Taproot Upgrade
The Taproot was the biggest upgrade in Bitcoin’s network after the SegWit upgrade in July 2017. Taproot introduced Schnorr signatures, which will help Bitcoin transactions become more private, efficient, and cost-efficient. This upgrade gave quite a boost to Lightning.
Read more: Previewing Bitcoin’s Latest Upgrade: the Taproot
Taproot makes it possible to make Lightning transactions look indistinguishable from normal transactions, making it much less clear that the user is using the Lightning Network for their transactions.
It could also pave the way for ?Point Lock Time Contracts?. The beauty of this is that they make it much harder for someone trying to trace a payment’s origin to link these various hops, shielding the path where a payment came from.
Lightning liquidity boosts
One of the biggest problems that Lightning faces is inbound liquidity.
To receive money on Lightning, users need to either spend money first or find some other way of obtaining ?inbound liquidity.? This is super confusing to newer users who are just there to accept payments easily.
At the end of 2020, Lightning Labs introduced Pool, a marketplace for buying and selling this essential liquidity, giving developers a better interface for tracking it down. In 2021, Lightning Labs also unveiled ‘sidecar channels,? an easy way to also use the marketplace to help others get inbound liquidity easily ? for a fee.
Fee-bumping jumps to the rescue
One of the problems we discussed above was transaction fees and how users have to pay a fee while opening and closing a channel. A user has to set an initial closing fee when they open the channel. But Bitcoin fees can fluctuate wildly. So, the fee a user decides to pay today could be too big or small for a transaction that closes, say, a year from now.
‘Anchor outputs‘ is a feature designed to make it possible to bump up such a fee. The Lightning Network’s three leading code implementations LND, C-lightning, and Eclair all implemented anchor outputs in some form in 2021.
Offers for a smoother user experience
Lightning payments are usually accepted with an invoice ? usually in the form of a QR code. However, this invoice can be used only once. Thus, every time you want to receive a new Lightning transaction, you need to generate a new invoice.
However, a proposal that gained steam in 2021 was ‘offers‘ championed by Blockstream Lightning developer Rusty Russell and standardized in BOLT 12. One reason Russell is pushing for offers is that it potentially offers better privacy. In addition to allowing multiple payments to the same address or QR code, offers will introduce a way to send recurring payments over the Lightning Network, such as a monthly payment to Netflix.
Improved Payment Routing Reliability
Another crucial issue is the reliability of Lightning payments.
Payments on the network don’t always go through properly, especially if they’re larger payments. The average Lightning channel capacity is currently around $2,033, meaning if you want to send payments above that amount, it will be more difficult to find a consistent path across the network.
Currently, the algorithm in Lightning focuses on finding the cheapest route for the user in terms of fees, which is also more likely to pick a path that fails. C-lightning has implemented an experimental first version of the new routing mechanism, which has successfully routed payments more reliably, as the authors of the paper hypothesized.
Final Thoughts
With all these changes churning, Lightning is growing easier to use, as well as more reliable and private.
In 2022, Lightning developers are looking to build upon these changes in the hopes that they trickle down to help everyday Lightning payment users. The Lightning Network may not be the solution to all of Bitcoin’s problems but it is an ever-evolving concept that is likely to make a significant difference to Bitcoin’s blockchain.
About Us
ImmuneBytes is a Blockchain security auditing firm that employs the industry’s best tools and practices to provide a comprehensive smart contract audit. We have a team of robust and experienced security professionals who are adept at their niches and provide you with quality service. We have worked on 165+ projects spread across the world on different Blockchain frameworks with some of the industry’s top firms and we continue to unfold the decentralized movement.
We are also providing consultancy, coming up with a bug bounty platform, and also an insurance product to provide our clients with a hassle-free security product catalog. Stay tuned.

