Post Ethereum entry into the web3 space, smart contracts rose at the top of the blockchain hierarchy, having the widest possible use cases. But, probably, Ethereum wasn’t sufficient to cater to a vast user base with diverse expectations. This was when other layer1, layer2 sidechains, zk.rollups, and more came in.
One such (Ethereum virtual machine) EVM-compatible Binance smart chain came as a standalone blockchain running parallel to its precursor Binance chain.
Binance, one of the world’s most popular centralized crypto exchanges, facilitates its reach further into Defi with Binance Smart Chain. Launched in September 2020, BSC is an innovative solution to bring programmability and interoperability to Binance Chain.
BSC runs in tandem with Binance’s native Binance Chain (BC), giving users the best of both worlds: BC’s huge transaction capacity and BSC’s smart contract features.
This blog will dive deep into several aspects of the Binance smart chain, from its definition to working, comparison with the Binance chain, consensus mechanism, and more.
Let’s Begin!
What is the Binance Smart Chain?
Table of Contents
- 1 What is the Binance Smart Chain?
- 2 Binance Smart Chain Vs. Binance Chain
- 3 What are the Differences Between the Two?
- 4 How Does Binance Smart Chain Work?
- 5 Cross-Chain Compatibility
- 6 What makes BSC the talk of the town?
- 7 How is Binance Smart Chain different from Ethereum?
- 8 What is Binance Smart Chain Faucet?
- 9 Pros of Binance Smart chain
- 10 Cons of Binance Smart Chain
- 11 What does the Future Hold for BSC?
- 12 Wrap Up
Binance launched BSC Binance Smart Chain with the primary aim of facilitating fast, decentralized trading. The design goal of the developers was to leave the high throughput of the Binance Chain intact while introducing smart contracts into its ecosystem.
The two pillars of the Binance smart chain network are EVM-compatible smart contracts and protocols. This dual-chain architecture empowers users to build their decentralized apps and digital assets on one blockchain while availing the advantage of fast trading to exchange on the other. It makes cross-chain transfer and other communication possible due to native interoperability support.
Binance Smart Chain Vs. Binance Chain
To get a fair understanding of the Binance smart chain and Binance chain, let’s look at their similarities and differences.
How is BSC similar to BC?
- Both chains are launched by the world’s largest centralized exchange, Binance, and have considerable control over both, although to a different extent.
- Faster block time, significantly lower fees, and high throughput.
What are the Differences Between the Two?
- Binance chain is limited in functionality, hosting Binance DEX, while Binance smart chain being a programmable platform, has a broader use case and supports smart contract deployment on the blockchain network.
- While BSC validates network transactions using proof of staking authority (see below), BC employs the Tendermint BFT consensus technique. At BC, Binance exchange controls the network without any community involvement.
- BC network tokens are generated in accordance with the BEP-2 issuance standard, whereas the Binance smart chain coins must adhere to BEP-20 regulations.
How Does Binance Smart Chain Work?
Consensus
BSC supports proof of staked authority mechanism to achieve consensus within its network. Proof of staked authority is an integrated concept of delegated proof of stake( DPoS) and proof of authority(PoA).
In DPoS, token holders can become validators by staking their BSC network native tokens. With DPoS, anyone with the minimum required tokens can become a validator. While in PoA, the validators are chosen by a central party, which in this case is Binance.
A system of 21 validators with Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus supports a shorter block time, lower fees, and higher throughput to fuel up the Binance smart chain. The most bonded validator candidates of staking become the validators to validate transactions and produce blocks to receive the transaction fees when they validate approved blocks on the network.
Cross-Chain Compatibility
BSC offers cross-chain compatibility to allow seamless asset transfer between blockchains. Here users can engage in data transfer between Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain and create ?pegged coins? (from the list of Binance smart chain coins), including BTC, ETH, TRX, and more.
Being compatible with EVM, it bargains with the support for the rich universe of Ethereum tools and decentralized applications, DApps. Theoretically, this could be particularly appealing to the developers as it makes porting their projects from Ethereum uncomplicated.
Applications like Metamask wallet, a crypto wallet & gateway to blockchain apps, can be easily configured to work with BSC. All you have to do is tweak a few settings and make it work!
As mentioned, Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain networks are intended to work in unison and have easy cross-chain compatibility. It is also an independent blockchain that could run even if Binance Chain went offline.?
What makes BSC the talk of the town?
The features that make Binance Smart Chain popular amongst crypto enthusiasts are:
- A self-sovereign blockchain that provides security and safety with elected validators.
- EVM-compatible.
- It comes with efficient native dual-chain communication optimized for scaling high-performance dApps.
- Distributed with on-chain governance: PoSA brings in decentralization and community participants. As the native token, BNB serves as both the gas of smart contract execution and tokens for staking.
- With a ~5-second block time, BSC enables high-speed transactions that only cost network participants a few cents.
Let’s look at some BSC metrics to get a clearer picture.
- Looking at Binance Smart Chain?Daily Transactions Count?gives an idea of the network’s activity.
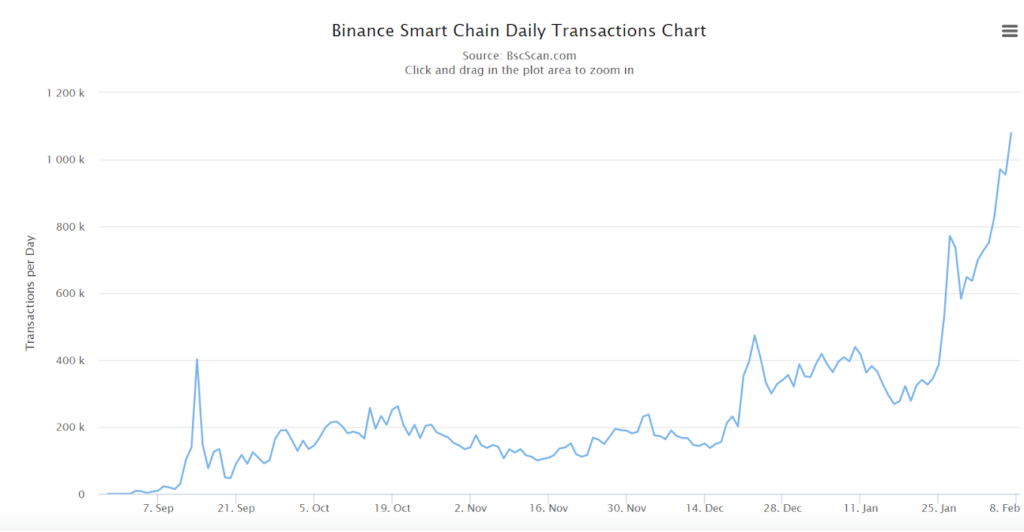
Source: https://bscscan.com/chart/tx
- This next one represents the Binance Smart Chain?Unique Address Count,?by which we can gauge roughly how many users the blockchain has.
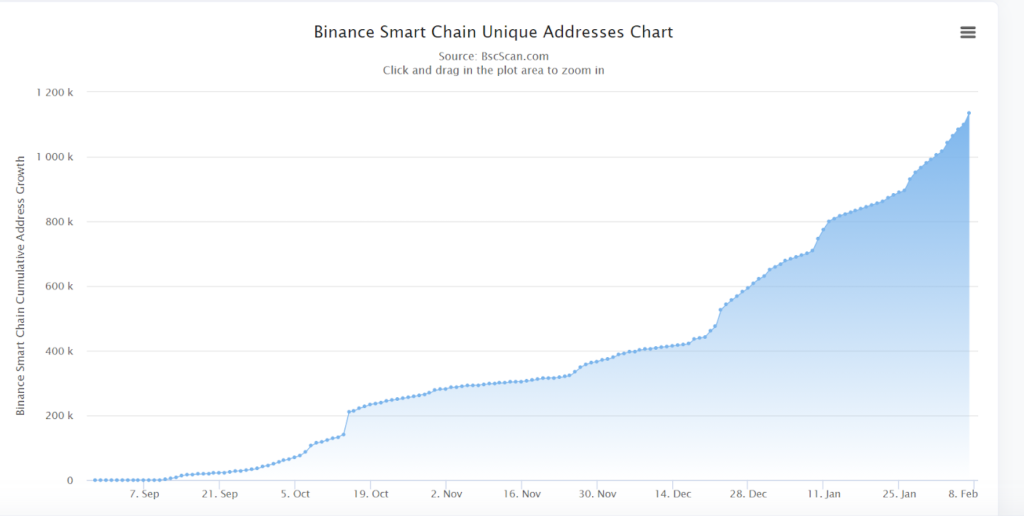
Source: https://bscscan.com/chart/address
Decentralized applications built on Binance Smart Chain have already experienced substantial user uptake, with DeFi apps leading the foray.
How is Binance Smart Chain different from Ethereum?
Decentralized applications built on Binance Smart Chain have already experienced substantial user uptake, with Defi apps leading the foray.
Before the introduction of Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Ethereum dominated the blockchain ecosystem, particularly in the smart contract space. However, as Binance Smart Chain gains traction in the Defi sector, it is now emerging as the most significant competitor.
Let’s look at the few differences between BSC and Ethereum networks.
- Ethereum, before the merge, is based on PoW consensus, while BSC uses the Proof of Staked Authority consensus mechanism.
- The cost of transactions is higher on the Ethereum network than on BSC.
- BSC has a much lower transaction time than the Ethereum network( BSC~ 3 sec, Ethereum~ 13 sec)
- Due to blockchain interoperability, many decentralized finance DApps move between Ethereum and BSC networks. The transition of apps from Ethereum to BSC is simpler for developers.
What is Binance Smart Chain Faucet?
Binance Smart Chain Faucet is a portal where developers can access test tokens, including BNB, BUSC, and BTC, on the testnet ecosystem.
These tokens are to be claimed free of cost by the developers to deploy smart contracts on the testnet.
To get the Binance testnet faucet, you only need to add testnet cash to your testnet account. Navigate to the testnet faucet. Log in to your Binance account. You will receive 200 Testnet BNB as soon as you finish this step, making it simpler to communicate with the Binance DEX testnet.
Additional Resource: Binance Smart Chain Faucet
Pros of Binance Smart chain
Launched only in 2020, BSC has seen a sharp rise in the user base in a short span of time. Here are a few benefits of the Binance smart chain that makes it a popular choice amongst its users.
- Low Binance smart chain transaction per second
Source:https://ycharts.com/indicators/binance_smart_chain_average_transaction_fee
- Backed by a centralized Binance network, a large user base of Binance led to faster adoption of the Binance smart chain network.
- With several cross-chain bridges existing on the platform, BSC users can easily transfer their tokens from one network to another.
Cons of Binance Smart Chain
Since every coin has a flip side, Binance smart chain is not without demerits attached to its network. Here are some of the cons of the BSC network.
- Launched as an EVM-compatible smart chain, it depends on the Ethereum development community that acts as a pathway for every innovation in the network.
- Centralized nature adopted from its parent network Binance.
- Security issues with Ethereum Binance also face many cyber attacks on its platform.
What does the Future Hold for BSC?
BSC is a reliable blockchain network even if it, perhaps, offers less innovation than Ethereum. The blockchain went from handling ten thousand transactions per day less than a year after its introduction.
Backed up by Binance’s $100 million support fund for developers building on BSC and its high adoption rate worldwide, it’s hard to imagine the current growth trajectory slowing down anytime soon. Binance Smart Chain’s flexibility and smart contract functionality will help the Defi world grow and reach new heights.?
But with the increasing popularity of BSC, it is imperative to cater to the security domain of the BSC network. A BSC audit is probably the first step in that direction. Binance smart chain audit provides security coverage to your Binance smart contract to keep it away from hackers and improve performance.
Wrap Up
BSC was established just before the Defi revolution as interest in blockchain-powered alternative financial solutions and used cases among the general population grew. Today, BNB continues to connect Binance and BSC.
Though still in its infancy, BSC looks promising and is heading toward establishing itself as a user-friendly alternative for the largely Ethereum-based Defi market.?
Additional Resource

